Potential clinical utility of liquid biopsies in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 35545786
- PMCID: PMC9092780
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01588-8
Potential clinical utility of liquid biopsies in ovarian cancer
Abstract
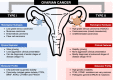
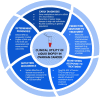
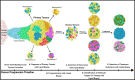
Ovarian cancer (OC) is the most lethal gynecologic malignancy worldwide. One of the main challenges in the management of OC is the late clinical presentation of disease that results in poor survival. Conventional tissue biopsy methods and serological biomarkers such as CA-125 have limited clinical applications. Liquid biopsy is a novel sampling method that analyzes distinctive tumour components released into the peripheral circulation, including circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA), circulating tumour cells (CTCs), cell-free RNA (cfRNA), tumour-educated platelets (TEPs) and exosomes. Increasing evidence suggests that liquid biopsy could enhance the clinical management of OC by improving early diagnosis, predicting prognosis, detecting recurrence, and monitoring response to treatment. Capturing the unique tumour genetic landscape can also guide treatment decisions and the selection of appropriate targeted therapies. Key advantages of liquid biopsy include its non-invasive nature and feasibility, which allow for serial sampling and longitudinal monitoring of dynamic tumour changes over time. In this review, we outline the evidence for the clinical utility of each liquid biopsy component and review the advantages and current limitations of applying liquid biopsy in managing ovarian cancer. We also highlight future directions considering the current challenges and explore areas where more studies are warranted to elucidate its emerging clinical potential.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer: advantages and limitations for prognosis and diagnosis.Med Oncol. 2023 Aug 10;40(9):265. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02128-0. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37561363 Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer using circulating tumor DNA and cells: Ready for prime time?Cancer Lett. 2020 Jan 1;468:59-71. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.014. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31610267 Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer.Adv Clin Chem. 2020;97:13-71. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Adv Clin Chem. 2020. PMID: 32448432 Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in breast cancer: A comprehensive review.Clin Genet. 2019 Jun;95(6):643-660. doi: 10.1111/cge.13514. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Clin Genet. 2019. PMID: 30671931 Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer: recent advances on circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018 Jan 26;56(2):186-197. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2017-0019. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 28753534 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor therapeutics in the era of "RECIST": past, current insights, and future prospects.Oncol Rev. 2024 Oct 18;18:1435922. doi: 10.3389/or.2024.1435922. eCollection 2024. Oncol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39493769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic role of circulating tumor DNA across breast cancer molecular subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Natl Cancer Cent. 2024 May 3;4(2):153-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2024.04.005. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Natl Cancer Cent. 2024. PMID: 39282586 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian cancer: Diagnosis and treatment strategies (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 18;28(3):441. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14574. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39099583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: A potential tool for immunotherapy of ovarian cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 18;13:1089410. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1089410. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36741380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"DEPHENCE" system-a novel regimen of therapy that is urgently needed in the high-grade serous ovarian cancer-a focus on anti-cancer stem cell and anti-tumor microenvironment targeted therapies.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 28;13:1201497. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1201497. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37448521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

