Retracted Article: Upregulation of miR-26b alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting BDNF via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in rats
- PMID: 35540064
- PMCID: PMC9076454
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06264e
Retracted Article: Upregulation of miR-26b alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting BDNF via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in rats
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Upregulation of miR-26b alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting BDNF via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in rats.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 20;11(7):4231. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90020j. eCollection 2021 Jan 19. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35427020 Free PMC article.
Abstract
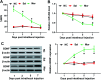
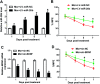
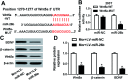
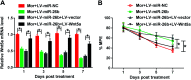
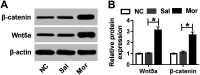
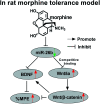
Background: Morphine is a commonly used analgesic drug. However, long-term use of morphine will cause tolerance which limits its clinical application in pain treatment. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to be involved in the morphine tolerance, but the underlying mechanism is still poorly understood. Methods: Tail flick test was used to measure the maximum possible effect (MPE). Quantitative real-time PCR was employed to detect miR-26b, BDNF, and Wnt5a expression in rat dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Luciferase report assay was introduced to verify the binding relationship between miR-26b and Wnt5a. BDNF, Wnt5a and β-catenin protein level were tested by western blotting. Results: MiR-26b was down-regulated during the development of morphine tolerance while BDNF was upregulated. Overexpression of miR-26b or BDNF inhibition alleviated morphine tolerance. Wnt5a was directly targeted and inhibited by miR-26b via binding to the 3'-UTR of Wnt5a. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway was active in morphine tolerant rats. Moreover, overexpression of Wnt5a could partially enhance miR-26 mimic-mediated morphine tolerance, while a Wnt5a inhibitor could attenuate the tolerance. Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that miR-26b overexpression alleviated morphine tolerance by inhibiting BDNF via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in rats, highlighting a promising target for the treatment of morphine tolerance.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest is declared by all named co-authors.
Figures
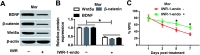
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-26b inhibits cell proliferation and cytokine secretion in human RASF cells via the Wnt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway.Diagn Pathol. 2015 Jun 19;10:72. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0309-x. Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26088648 Free PMC article.
-
Retraction: Upregulation of miR-26b alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting BDNF via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in rats.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 20;11(7):4231. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90020j. eCollection 2021 Jan 19. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35427020 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-375 level ameliorates morphine analgesic tolerance in mouse dorsal root ganglia by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.J Pain Res. 2017 May 26;10:1279-1287. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S125264. eCollection 2017. J Pain Res. 2017. PMID: 28603428 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-365 alleviates morphine analgesic tolerance via the inactivation of the ERK/CREB signaling pathway by negatively targeting β-arrestin2.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Feb 7;25(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0405-9. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29415719 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-26b regulates cartilage differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;23(12):5084-5092. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18172. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31298408
References
-
- McQuay H. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2010;41:1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

