Interplay of SOX transcription factors and microRNAs in the brain under physiological and pathological conditions
- PMID: 35535866
- PMCID: PMC9120710
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.338990
Interplay of SOX transcription factors and microRNAs in the brain under physiological and pathological conditions
Abstract
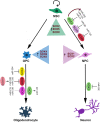
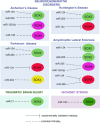
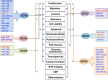
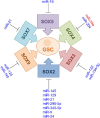
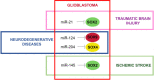
Precise tuning of gene expression, accomplished by regulatory networks of transcription factors, epigenetic modifiers, and microRNAs, is crucial for the proper neural development and function of the brain cells. The SOX transcription factors are involved in regulating diverse cellular processes during embryonic and adult neurogenesis, such as maintaining the cell stemness, cell proliferation, cell fate decisions, and terminal differentiation into neurons and glial cells. MicroRNAs represent a class of small non-coding RNAs that play important roles in the regulation of gene expression. Together with other gene regulatory factors, microRNAs regulate different processes during neurogenesis and orchestrate the spatial and temporal expression important for neurodevelopment. The emerging data point to a complex regulatory network between SOX transcription factors and microRNAs that govern distinct cellular activities in the developing and adult brain. Deregulated SOX/microRNA interplay in signaling pathways that influence the homeostasis and plasticity in the brain has been revealed in various brain pathologies, including neurodegenerative disorders, traumatic brain injury, and cancer. Therapeutic strategies that target SOX/microRNA interplay have emerged in recent years as a promising tool to target neural tissue regeneration and enhance neurorestoration. Numerous studies have confirmed complex interactions between microRNAs and SOX-specific mRNAs regulating key features of glioblastoma. Keeping in mind the crucial roles of SOX genes and microRNAs in neural development, we focus this review on SOX/microRNAs interplay in the brain during development and adulthood in physiological and pathological conditions. Special focus was made on their interplay in brain pathologies to summarize current knowledge and highlight potential future development of molecular therapies.
Keywords: SOX/miRNA interplay; dysregulation of miRNA expression; glioblastoma; gliogenesis; glioma stem cells; ischemic stroke; neural stem cells; neural tissue regeneration; neurodegenerative diseases; neurodevelopment; neurogenesis; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
SOX Transcription Factors as Important Regulators of Neuronal and Glial Differentiation During Nervous System Development and Adult Neurogenesis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Mar 31;14:654031. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.654031. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33867936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA regulation of neural stem cells and neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 10;30(45):14931-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4280-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21068294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional mechanisms controlling neurogenesis and direct neuronal reprogramming.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):1929-1939. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390976. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38227517 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the ubiquitous role of microRNAs in neurogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):2003-2011. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9797-2. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26910816 Review.
-
The roles of MicroRNAs in neural regenerative medicine.Exp Neurol. 2020 Oct;332:113394. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113394. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32628967 Review.
Cited by
-
Stage-specific expression patterns and co-targeting relationships among miRNAs in the developing mouse cerebral cortex.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 22;7(1):1366. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07092-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39433948 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Evolution, and Expression Pattern Analysis of the GATA Gene Family in Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 17;23(20):12434. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012434. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293290 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of SOX Transcription Factors in Ageing and Age-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):851. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010851. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Epigenetics in Neuroinflammatory-Driven Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 2;23(23):15218. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315218. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of glioblastoma's resistance: investigating the influence of tumor suppressor p53 and non-coding RNAs.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 30. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03564-z. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39476245 Review.
References
-
- Angelopoulou E, Paudel YN, Piperi C. miR-124 and Parkinson's disease: a biomarker with therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Res. 2019;150:104515. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

