Retracted Article: Elevation of USP4 antagonizes oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-evoked microglia activation and neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity via the TRAF6-NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 35530618
- PMCID: PMC9069457
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03614h
Retracted Article: Elevation of USP4 antagonizes oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-evoked microglia activation and neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity via the TRAF6-NF-κB signaling
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Elevation of USP4 antagonizes oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-evoked microglia activation and neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity via the TRAF6-NF-κB signaling.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 21;11(8):4374. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90021h. eCollection 2021 Jan 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35426983 Free PMC article.
Abstract
An ischemic stroke is a devastating neurological disease with the typical occurrence of brain ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, and it has high mortality and disability globally. Microglia activation after a stroke results in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that can further aggravate brain damage. A recent study confirmed the potential role of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 4 (USP4) in the injury process. Nevertheless, the role and mechanism of USP4 during an ischemic stroke remain elusive. In this research, we simulated an I/R injury by oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) in vitro and confirmed the obvious down-regulation of USP4 in microglia under OGD/R conditions. Moreover, USP4 elevation antagonized the OGD/R-induced microglia proliferation and activation by suppressing the NO levels and the expression of the microglial marker IBA-1. Additionally, the overexpression of USP4 suppressed the release of microglia activation-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. Intriguingly, incubation with the conditioned medium from the microglia under OGD/R conditions induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting cell viability and increasing the LDH release, apoptosis, and caspase-3 activity, which were reversed following USP4 overexpression. Mechanism analysis corroborated that USP4 up-regulation repressed the OGD/R-induced activation of TRAF6-NF-κB signaling. Notably, restoring the TRAF6 signaling ameliorated the suppressive effects of USP4 elevation on microglia activation, inflammation, and the subsequent neuron injury. These findings suggest that USP4 may alleviate ischemic stroke by restraining microglia-mediated neuro-inflammation and neurotoxicity via the TRAF6-NF-κB pathway, due to which it is a promising therapeutic agent against strokes.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
Figures
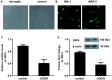
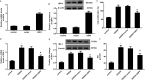
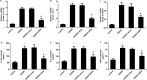
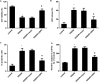
Similar articles
-
Administration with curcumin alleviates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating anti-oxidative stress and microglia activation-mediated neuroinflammation via Nrf2/NF-κB axis.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 Mar;60(2):172-182. doi: 10.1007/s11626-023-00846-3. Epub 2024 Jan 16. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38228998
-
Downregulation of USP4 Promotes Activation of Microglia and Subsequent Neuronal Inflammation in Rat Spinal Cord After Injury.Neurochem Res. 2017 Nov;42(11):3245-3253. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2361-2. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 28755289
-
Retraction: Elevation of USP4 antagonizes oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-evoked microglia activation and neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity via the TRAF6-NF-κB signaling.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 21;11(8):4374. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90021h. eCollection 2021 Jan 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35426983 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid inhibits HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB signaling to alleviate oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury of microglia.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Feb 12;540:22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.12.097. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33429196
-
Exploring Chinese herbal medicine for ischemic stroke: insights into microglia and signaling pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1333006. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1333006. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38318134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Demaerschalk B. M. Hwang H. M. Leung G. US cost burden of ischemic stroke: a systematic literature review. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2010;16:525–533. - PubMed
-
- Godinho J. de Sa-Nakanishi A. B. Moreira L. S. de Oliveira R. M. W. Huzita C. H. Mello J. C. P. da Silva A. O. F. Nakamura C. V. Previdelli I. S. Ribeiro M. Milani H. Ethyl-acetate fraction of Trichilia catigua protects against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018;221:109–118. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

