Anthelmintics nitazoxanide protects against experimental hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in hamsters and mice
- PMID: 35530137
- PMCID: PMC9069401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.009
Anthelmintics nitazoxanide protects against experimental hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis in hamsters and mice
Abstract
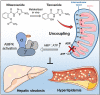
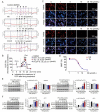
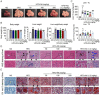
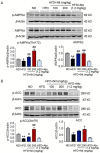
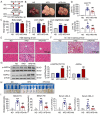
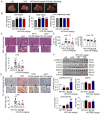
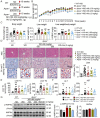
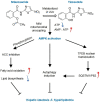
Lipid metabolism disorders contribute to hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis. It is ideal to develop drugs simultaneous improving both hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis. Nitazoxanide is an FDA-approved oral antiprotozoal drug with excellent pharmacokinetic and safety profile. We found that nitazoxanide and its metabolite tizoxanide induced mild mitochondrial uncoupling and subsequently activated AMPK in HepG2 cells. Gavage administration of nitazoxanide inhibited high-fat diet (HFD)-induced increases of liver weight, blood and liver lipids, and ameliorated HFD-induced renal lipid accumulation in hamsters. Nitazoxanide significantly improved HFD-induced histopathologic changes of hamster livers. In the hamsters with pre-existing hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis, nitazoxanide also showed therapeutic effect. Gavage administration of nitazoxanide improved HFD-induced hepatic steatosis in C57BL/6J mice and western diet (WD)-induced hepatic steatosis in Apoe -/- mice. The present study suggests that repurposing nitazoxanide as a drug for hyperlipidemia and hepatic steatosis treatment is promising.
Keywords: AMPK; Autophagy; Hepatic steatosis; Hyperlipidemia; Mitochondrial uncoupling; Nitazoxanide; SQSTM1/P62; Tizoxanide.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The clinical antiprotozoal drug nitazoxanide and its metabolite tizoxanide extend Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan and healthspan.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Jul;14(7):3266-3280. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.031. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39027239 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing nitazoxanide as a novel anti-atherosclerotic drug based on mitochondrial uncoupling mechanisms.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Jan;180(1):62-79. doi: 10.1111/bph.15949. Epub 2022 Oct 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36082580
-
Nitazoxanide protects against experimental ulcerative colitis through improving intestinal barrier and inhibiting inflammation.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 May 25;395:111013. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111013. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38663798
-
Anthelmintic nitazoxanide protects against experimental pulmonary fibrosis.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;180(23):3008-3023. doi: 10.1111/bph.16190. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37428102
-
Gracilaria chorda subcritical water ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and regulates glucose homeostasis in a hepatic steatosis cell model and obese C57BL/6J mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Feb 10;320:117395. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117395. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37952731
Cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Emerging Targets and Drug Candidates.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 26;10(2):274. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020274. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical antiprotozoal drug nitazoxanide and its metabolite tizoxanide extend Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan and healthspan.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Jul;14(7):3266-3280. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.031. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39027239 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic and lipidomic studies on the intervention of taurochenodeoxycholic acid in mice with hyperlipidemia.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 15;14:1255931. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1255931. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38034994 Free PMC article.
-
Schisanhenol ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via inhibiting miR-802 activation of AMPK-mediated modulation of hepatic lipid metabolism.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Sep;14(9):3949-3963. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.014. Epub 2024 May 17. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39309511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eslam M., Newsome P.N., Sarin S.K., Anstee Q.M., Targher G., Romero-Gomez M., et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73:202–209. - PubMed
-
- Eslam M., Sanyal A.J., George J., International Consensus P. Mafld: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1999–2014. e1. - PubMed
-
- Weber C., Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. 2011;17:1410–1422. - PubMed
-
- Ouchi Y., Sasaki J., Arai H., Yokote K., Harada K., Katayama Y., et al. Ezetimibe lipid-lowering trial on prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in 75 or older (ewtopia 75): a randomized, controlled trial. Circulation. 2019;140:992–1003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

