Novel Biomarkers in Membranous Nephropathy
- PMID: 35529848
- PMCID: PMC9074781
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845767
Novel Biomarkers in Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
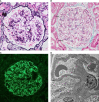
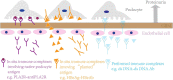
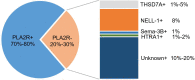
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is the main cause of adult nephrotic syndrome (NS). The pathogenesis of MN is complex and involves subepithelial immune complex deposition. Approximately one-third of patients with MN develop end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Timely diagnosis and reasonable intervention are the keys to improving prognosis. In recent years, with the development of high-throughput technologies, such as mass spectrometry (MS), microarray, and sequencing technologies, the discovery of biomarkers for MN has become an important area of research. In this review, we summarize the significant progress in biomarker identification. For example, a variety of podocyte target antigens and their autoantibodies have been reported. Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) is the most well-established target antigen in MN. PLA2R and its autoantibodies have clinical significance, with both diagnostic and therapeutic value for MN. In addition, a variety of new biomarkers, including proteins, metabolites, noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), and immune cells, have recently been found. These MN-related biomarkers have great significance in the diagnosis, progression, prognosis, and treatment response of MN.
Keywords: biomarker; immune cell; membranous nephropathy; metabolome; noncoding RNA; phospholipase A2 receptor; proteome.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Liu, Lin, Zhang, Ma, Yang and Qin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Membranous nephropathy-diagnosis and identification of target antigens.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Mar 27;39(4):600-606. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad227. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 37863839 Review.
-
Circulating antibodies to α-enolase and phospholipase A2 receptor and composition of glomerular deposits in Japanese patients with primary or secondary membranous nephropathy.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017 Feb;21(1):117-126. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1235-2. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 26830547 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerating the Depletion of Circulating Anti-Phospholipase A2 Receptor Antibodies in Patients with Severe Membranous Nephropathy: Preliminary Findings with Double Filtration Plasmapheresis and Ofatumumab.Nephron. 2020;144(1):30-35. doi: 10.1159/000501858. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Nephron. 2020. PMID: 31336376
-
A comprehensive narrative review of diagnostic biomarkers in human primary membranous nephropathy.Biomark Med. 2017 Sep;11(9):781-797. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0081. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Biomark Med. 2017. PMID: 28891307 Review.
-
Diagnostic specificity of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) in differentiating idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN) from secondary forms and other glomerular diseases.J Nephrol. 2018 Apr;31(2):271-278. doi: 10.1007/s40620-017-0451-5. Epub 2017 Oct 28. J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29081027
Cited by
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for identifying fibroblast-associated biomarkers and molecular subtypes in human membranous nephropathy.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 25;10(21):e38424. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38424. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524772 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppressive Agent Options for Primary Nephrotic Syndrome: A Review of Network Meta-Analyses and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Mar 17;59(3):601. doi: 10.3390/medicina59030601. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36984602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Future embracing: exosomes driving a revolutionary approach to the diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 8;22(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02633-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39118155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards the Definition of the Molecular Hallmarks of Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy in Serum Proteome: A DIA-PASEF Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 21;24(14):11756. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411756. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511514 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of glomeruli, tubules and renal interstitium in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN): A statistically observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 15;102(50):e36476. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036476. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38115247 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

