Deuteration versus ethylation - strategies to improve the metabolic fate of an 18F-labeled celecoxib derivative
- PMID: 35517533
- PMCID: PMC9057277
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04494f
Deuteration versus ethylation - strategies to improve the metabolic fate of an 18F-labeled celecoxib derivative
Abstract
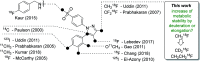
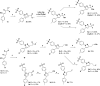
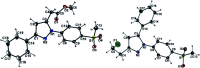
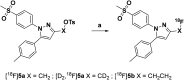
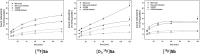
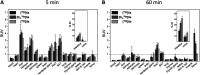
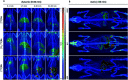
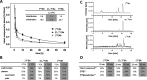
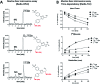
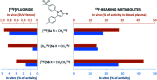
The inducible isoenzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is closely associated with chemo-/radioresistance and poor prognosis of solid tumors. Therefore, COX-2 represents an attractive target for functional characterization of tumors by positron emission tomography (PET). In this study, the celecoxib derivative 3-([18F]fluoromethyl)-1-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-5-(p-tolyl)-1H-pyrazole ([18F]5a) was chosen as a lead compound having a reported high COX-2 inhibitory potency and a potentially low carbonic anhydrase binding tendency. The respective deuterated analog [D2,18F]5a and the fluoroethyl-substituted derivative [18F]5b were selected to study the influence of these modifications with respect to COX inhibition potency in vitro and metabolic stability of the radiolabeled tracers in vivo. COX-2 inhibitory potency was found to be influenced by elongation of the side chain but, as expected, not by deuteration. An automated radiosynthesis comprising 18F-fluorination and purification under comparable conditions provided the radiotracers [18F]5a,b and [D2,18F]5a in good radiochemical yields (RCY) and high radiochemical purity (RCP). Biodistribution and PET studies comparing all three compounds revealed bone accumulation of 18F-activity to be lowest for the ethyl derivative [18F]5b. However, the deuterated analog [D2,18F]5a turned out to be the most stable compound of the three derivatives studied here. Time-dependent degradation of [18F]5a,b and [D2,18F]5a after incubation in murine liver microsomes was in accordance with the data on metabolism in vivo. Furthermore, metabolites were identified based on UPLC-MS/MS.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of structural alterations on the radiopharmacological profile of 18F-labeled pyrimidines as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) imaging agents.Nucl Med Biol. 2018 Jul-Aug;62-63:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 5. Nucl Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29800798
-
Synthesis, biodistribution and PET studies in rats of (18)F-Labeled bridgehead fluoromethyl analogues of WAY-100635.Nucl Med Biol. 2012 Oct;39(7):1068-76. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 May 17. Nucl Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22609028
-
Fluorine-18-Labeled PET Radiotracers for Imaging Tryptophan Uptake and Metabolism: a Systematic Review.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Aug;22(4):805-819. doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01430-6. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 31512038 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosynthesis and Biological Evaluation of [18F]Triacoxib: A New Radiotracer for PET Imaging of COX-2.Mol Pharm. 2020 Jan 6;17(1):251-261. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00986. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31816246
-
Fluorinated PET Tracers for Molecular Imaging of σ1 Receptors in the Central Nervous System.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;964:31-48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28315263 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of Radiotracer Metabolic Stability In Vitro with CYP-Overexpressing Hepatoma Cell Lines.Cells. 2022 Aug 7;11(15):2447. doi: 10.3390/cells11152447. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35954291 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of 18F-Labeled Tracers Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein via Sulfur [18F]Fluoride Exchange Reaction.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 10;15(12):2749. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122749. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140090 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of γ-Secretase Activity by a Carborane-Based Flurbiprofen Analogue.Molecules. 2021 May 11;26(10):2843. doi: 10.3390/molecules26102843. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34064783 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of an 18F-labeled Nε-acryloyllysine piperazide for covalent targeting of transglutaminase 2.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024 Jan 2;9(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s41181-023-00231-1. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024. PMID: 38165538 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorine-18 Labelled Radioligands for PET Imaging of Cyclooxygenase-2.Molecules. 2022 Jun 9;27(12):3722. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123722. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

