Modified lipid metabolism and cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation in mesangial cells under pro-inflammatory conditions
- PMID: 35513427
- PMCID: PMC9072365
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10907-4
Modified lipid metabolism and cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation in mesangial cells under pro-inflammatory conditions
Abstract
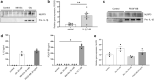
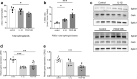
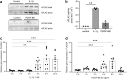
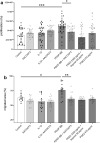
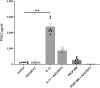
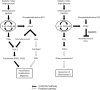
Diabetic kidney disease is a consequence of hyperglycemia and other complex events driven by early glomerular hemodynamic changes and a progressive expansion of the mesangium. The molecular mechanisms behind the pathophysiological alterations of the mesangium are yet to be elucidated. This study aimed at investigating whether lipid signaling might be the missing link. Stimulation of human mesangial cells with high glucose primed the inflammasome-driven interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) secretion, which in turn stimulated platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB) release. Finally, PDGF-BB increased IL-1β secretion synergistically. Both IL-1β and PDGF-BB stimulation triggered the formation of phosphorylated sphingoid bases, as shown by lipidomics, and activated cytosolic phospholipase cPLA2, sphingosine kinase 1, cyclooxygenase 2, and autotaxin. This led to the release of arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidylcholine, activating the secretion of vasodilatory prostaglandins and proliferative lysophosphatidic acids. Blocking cPLA2 release of arachidonic acid reduced mesangial cells proliferation and prostaglandin secretion. Validation was performed in silico using the Nephroseq database and a glomerular transcriptomic database. In conclusion, hyperglycemia primes glomerular inflammatory and proliferative stimuli triggering lipid metabolism modifications in human mesangial cells. The upregulation of cPLA2 was critical in this setting. Its inhibition reduced mesangial secretion of prostaglandins and proliferation, making it a potential therapeutical target.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
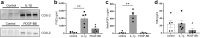
Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between secretory phospholipase A2 and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in rat renal mesangial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Oct 18;1348(3):257-72. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(97)00073-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997. PMID: 9366243
-
Interleukin 1 alpha causes rapid activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by phosphorylation in rat mesangial cells.J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1224-33. doi: 10.1172/JCI117076. J Clin Invest. 1994. PMID: 8132762 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1 beta and transforming growth factor-beta 2 enhance cytosolic high-molecular-mass phospholipase A2 activity and induce prostaglandin E2 formation in rat mesangial cells.Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):169-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17405.x. Eur J Biochem. 1992. PMID: 1446669
-
Platelet-derived growth factor and fibroblast growth factor differentially regulate interleukin 1beta- and cAMP-induced nitric oxide synthase expression in rat renal mesangial cells.J Clin Invest. 1997 Dec 1;100(11):2800-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI119827. J Clin Invest. 1997. PMID: 9389745 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of rat kidney mesangial cell phospholipase A2.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996 Jan;23(1):71-5. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8713499 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut-kidney axis in IgA nephropathy: Role on mesangial cell metabolism and inflammation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 17;10:993716. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.993716. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36467425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terminalia ferdinandiana Exell. extracts reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine and PGE2 secretion, decrease COX-2 expression and down-regulate cytosolic NF-κB levels.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Jun;32(3):1839-1853. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01462-7. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38581641 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Profile of Lin-Sca1+c-kit (LSK) cells in db/db mice with long-standing diabetes.BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 12;25(1):782. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10679-3. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39134978 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Palmitoylethanolamide in the Treatment of Long COVID: A Real-Life Retrospective Cohort Study.Med Sci (Basel). 2022 Jul 14;10(3):37. doi: 10.3390/medsci10030037. Med Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gouda W, Mageed L, Abd El Dayem SM, Ashour E, Afify M. Evaluation of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Bull. Natl. Res. Centre. 2018;42:14. doi: 10.1186/s42269-018-0016-3. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

