Blood Lipid Responses to Diets Enriched with Cottonseed Oil Compared With Olive Oil in Adults with High Cholesterol in a Randomized Trial
- PMID: 35511204
- PMCID: PMC9449680
- DOI: 10.1093/jn/nxac099
Blood Lipid Responses to Diets Enriched with Cottonseed Oil Compared With Olive Oil in Adults with High Cholesterol in a Randomized Trial
Abstract
Background: Increasing unsaturated fat intake is beneficial for cardiovascular health, but the type of unsaturated fat to recommend remains equivocal.
Objectives: We investigated the effects of an 8-week diet intervention that was rich in either cottonseed oil (CSO; PUFA rich) or olive oil (OO; MUFA rich) on blood lipids in hypercholesterolemic adults.
Methods: Forty-three men and women with hypercholesterolemia (53 ± 10 years; BMI, 27.6 ± 4.8 kg/m2) completed this randomized parallel clinical trial consisting of an 8-week partial outpatient feeding intervention. Participants were given meals and snacks accounting for ∼60% of their daily energy needs, with 30% of energy needs from either CSO (n = 21) or OO (n = 22). At pre- and postdiet intervention visits, participants consumed a high-SFA meal (35% of total energy needs; 70% of energy from fat). The primary outcomes of fasting cholesterol profiles and secondary outcomes of postprandial blood lipids and glycemic markers were assessed over a 5-hour period.
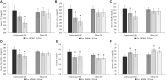
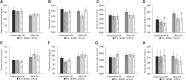
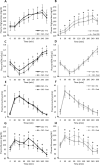
Results: There were greater reductions from baseline to week 8 in fasting serum total cholesterol (TC; -17.0 ± 3.94 mg/dL compared with -2.18 ± 3.72 mg/dL, respectively; P = 0.008), LDL cholesterol (-19.7 ± 3.94 mg/dL compared with -5.72 ± 4.23 mg/dL, respectively; P = 0.018), non-HDL cholesterol (-20.8 mg/dL ± 4.00 compared with -6.61 ± 4.01 mg/dL, respectively; P = 0.014), and apoB (-11.8 mg/dL ± 2.37 compared with -3.10 ± 2.99 mg/dL, respectively; P = 0.05), in CSO compared with OO. There were also visit effects from baseline to week 8 for increases in HDL cholesterol (CSO, 56.5 ± 2.79 mg/dL to 60.2 ± 3.35 mg/dL, respectively; OO: 59.7 ± 2.63 mg/dL to 64.1 ± 2.24 mg/dL, respectively; P < 0.001), and decreases in the TC:HDL-cholesterol ratio (CSO, 4.30 ± 0.27 mg/dL to 3.78 ± 0.27 mg/dL, respectively; OO, 3.94 ± 0.16 mg/dL to 3.57 ± 0.11 mg/dL, respectively; P < 0.001), regardless of group assignment. In response to the high-SFA meal, there were differences in postprandial plasma glucose (P = 0.003) and triglyceride (P = 0.004) responses and a trend in nonesterified fatty acids (P = 0.11) between groups, showing protection in the postprandial state from an occasional high-SFA fat meal with CSO, but not OO, diet enrichment.
Conclusions: CSO, but not OO, diet enrichment caused substantial improvements in fasting and postprandial blood lipids and postprandial glycemia in hypercholesterolemic adults. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT04397055.
Keywords: HDL cholesterol; LDL cholesterol; SCD1; cottonseed oil; high-fat diet; hypercholesterolemia; olive oil; stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Nutrition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A 5-day high-fat diet rich in cottonseed oil improves cholesterol profiles and triglycerides compared to olive oil in healthy men.Nutr Res. 2018 Dec;60:43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 9. Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 30527259 Clinical Trial.
-
Eight weeks of daily cottonseed oil intake attenuates postprandial angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4 responses compared to olive oil in adults with hypercholesterolemia: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial.Nutr Res. 2024 Mar;123:88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2024.01.006. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 38295507 Clinical Trial.
-
No Observed Difference in Inflammatory and Coagulation Markers Following Diets Rich in n-6 Polyunsaturated Fat vs Monounsaturated Fat in Adults With Untreated Hypercholesterolemia: A Randomized Trial.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2024 Feb;124(2):205-214.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2023.08.127. Epub 2023 Aug 22. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2024. PMID: 37619782 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of olive oil consumption on blood lipids: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Br J Nutr. 2023 Aug 28;130(4):728-736. doi: 10.1017/S0007114522003683. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Br J Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36408701 Review.
-
Olive Oil Polyphenols Improve HDL Cholesterol and Promote Maintenance of Lipid Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 6;13(12):1187. doi: 10.3390/metabo13121187. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38132869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is There More to Olive Oil than Healthy Lipids?Nutrients. 2023 Aug 18;15(16):3625. doi: 10.3390/nu15163625. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37630815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Meal-Timing on the Association of Unsaturated Fatty Acids with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality among Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study with 10-Year Follow-Up.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 28;16(13):2071. doi: 10.3390/nu16132071. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999822 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of cottonseed oil on lipids/lipoproteins: a systematic review and plasma cholesterol predictive equations estimations.Nutr Rev. 2024 Aug 1;82(8):1079-1086. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad109. Nutr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37695308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases....
-
- Kopin L, Lowenstein C. Dyslipidemia. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(11):ITC81–96. - PubMed
-
- Carroll MD, Fryar CD. Total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults: United States, 2015–2018. NCHS Data Brief, no 363. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2020.
-
- Mensink RP, Effects of saturated fatty acids on serum lipids and lipoproteins: A systematic review and regression analysis. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

