Microencapsulated probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and/or Pediococcus acidilactici strains ameliorate diarrhoea in piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 35505092
- PMCID: PMC9065055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11340-3
Microencapsulated probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and/or Pediococcus acidilactici strains ameliorate diarrhoea in piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
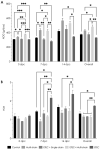
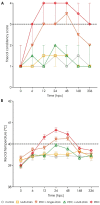
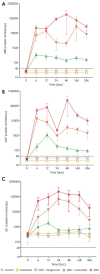
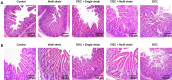
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (strains 22F and 25F) and Pediococcus acidilactici (strain 72N) have displayed antibacterial activity in vitro, suggesting that they could be used to support intestinal health in pigs. The aim of this study was to determine if microencapsulated probiotics could reduce the severity of infection with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in weaned pigs. Sixty healthy neonatal piglets were cross-fostered and separated into five groups. Piglets to be given the microencapsulated probiotics received these orally on days 0, 3, 6, 9, and 12. Only piglets in groups 1 and 5 did not receive probiotics: those in groups 2 and 4 received the three microencapsulated probiotic strains (multi-strain probiotic), and piglets in group 3 received microencapsulated P. acidilactici strain 72N. After weaning, the pigs in groups 3-5 were challenged with 5 mL (at 109 CFU/mL) of pathogenic ETEC strain L3.2 carrying the k88, staP, and stb virulence genes. The multi-strain probiotic enhanced the average daily gain (ADG) and feed conversion ratio (FCR) of weaned piglets after the ETEC challenge (group 4), whilst supplementing with the single-strain probiotic increased FCR (group 3). Piglets in groups 3 and 4 developed mild to moderate diarrhoea and fever. In the probiotic-fed piglets there was an increase in lactic acid bacteria count and a decrease in E. coli count in the faeces. By using real-time PCR, virulence genes were detected at lower levels in the faeces of pigs that had received the probiotic strains. Using the MILLIPLEX MAP assay, probiotic supplementation was shown to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, and TNFα), while group 4 had high levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10). Challenged piglets receiving probiotics had milder intestinal lesions with better morphology, including greater villous heights and villous height per crypt depth ratios, than pigs just receiving ETEC. In conclusion, prophylactic administration of microencapsulated probiotic strains may improve outcomes in weaned pigs with colibacillosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota in piglets either challenged or not with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli reveals beneficial effects of probiotics on microbiome composition, resistome, digestive function and oxidative stress responses.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 24;17(6):e0269959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269959. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35749527 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Lactobacillus plantarum (strains 22F and 25F) and Pediococcus acidilactici (strain 72N) as replacements for antibiotic-growth promotants in pigs.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 8;11(1):12028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91427-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34103574 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary fermented soybean meal replacement alleviates diarrhea in weaned piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 by modulating inflammatory cytokine levels and cecal microbiota composition.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Jul 14;16(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02466-5. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32664940 Free PMC article.
-
Small intestinal segment perfusion test in piglets: future applications in studying probiotics-gut crosstalk in infectious diarrhoea?Benef Microbes. 2010 Nov;1(4):439-45. doi: 10.3920/BM2010.0025. Benef Microbes. 2010. PMID: 21831782 Review.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and probiotics in swine: what the bleep do we know?Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2017;36(3):75-90. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.16-030. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2017. PMID: 28785529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dietary supplementation of Pediococcus pentosaceus strains from kimchi in weaned piglet challenged with Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica.J Anim Sci Technol. 2023 May;65(3):611-626. doi: 10.5187/jast.2023.e31. Epub 2023 May 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37332280 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid fermented cereals with added Pediococcus acidilactici did not reduce post-weaning diarrhea in pigs - an Escherichia coli challenge study.Front Vet Sci. 2023 May 12;10:1147165. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1147165. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37252380 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Zinc Oxide in Alleviating Diarrhea in Piglets after Weaning: A Review from the Perspective of Intestinal Barrier Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 18;25(18):10040. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810040. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of glucose oxidase on growth performance, clinical symptoms, serum parameters, and intestinal health in piglets challenged by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 3;13:994151. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.994151. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36267185 Free PMC article.
-
Panax notoginseng stems and leaves affect microbial community and function in cecum of duzang pigs.Transl Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 22;8:txad142. doi: 10.1093/tas/txad142. eCollection 2024. Transl Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38425544 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

