Extracting functional insights from loss-of-function screens using deep link prediction
- PMID: 35474966
- PMCID: PMC9017186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100171
Extracting functional insights from loss-of-function screens using deep link prediction
Abstract
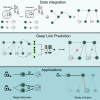
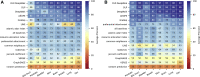
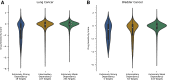
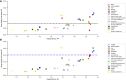
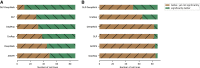
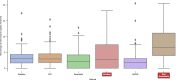
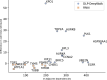
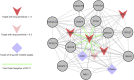
We present deep link prediction (DLP), a method for the interpretation of loss-of-function screens. Our approach uses representation-based link prediction to reprioritize phenotypic readouts by integrating screening experiments with gene-gene interaction networks. We validate on 2 different loss-of-function technologies, RNAi and CRISPR, using datasets obtained from DepMap. Extensive benchmarking shows that DLP-DeepWalk outperforms other methods in recovering cell-specific dependencies, achieving an average precision well above 90% across 7 different cancer types and on both RNAi and CRISPR data. We show that the genes ranked highest by DLP-DeepWalk are appreciably more enriched in drug targets compared to the ranking based on original screening scores. Interestingly, this enrichment is more pronounced on RNAi data compared to CRISPR data, consistent with the greater inherent noise of RNAi screens. Finally, we demonstrate how DLP-DeepWalk can infer the molecular mechanism through which putative targets trigger cell line mortality.
Keywords: CRISPR screening; PPI networks; bioinformatics; cancer cell lines; deep learning; drug targets; functional screening; link prediction; machine learning; systems biology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partial gene suppression improves identification of cancer vulnerabilities when CRISPR-Cas9 knockout is pan-lethal.Genome Biol. 2023 Aug 23;24(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03020-w. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37612728 Free PMC article.
-
Improved estimation of cancer dependencies from large-scale RNAi screens using model-based normalization and data integration.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 2;9(1):4610. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06916-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30389920 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring cancer dependencies on metabolic genes from large-scale genetic screens.BMC Biol. 2019 Apr 30;17(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0654-4. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 31039782 Free PMC article.
-
A Perspective on the Future of High-Throughput RNAi Screening: Will CRISPR Cut Out the Competition or Can RNAi Help Guide the Way?J Biomol Screen. 2015 Sep;20(8):1040-51. doi: 10.1177/1087057115590069. Epub 2015 Jun 5. J Biomol Screen. 2015. PMID: 26048892 Review.
-
Genome-wide CRISPR screens for the identification of therapeutic targets for cancer treatment.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Nov;24(11):1147-1158. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1820986. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32893711 Review.
References
-
- Bortone K., Michiels F., Vandeghinste N., Tomme P., van Es H. Functional screening of viral siRNA libraries in human primary cells. DDW Drug Discov. World. 2004;5:20–28.
-
- Braschi B., Denny P., Gray K., Jones T., Seal R., Tweedie S., Yates B., Bruford E. Genenames.org: the HGNC and VGNC resources in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D786–D792. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky930. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buitinck L., Louppe G., Blondel M., Pedregosa F., Mueller A., Grisel O., Niculae V., Prettenhofer P., Gramfort A., Grobler J., et al. API design for machine learning software: experiences from the Scikit-learn project. 2013. https://arxiv.org/abs/1309.0238
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

