Body composition and myokines in a cohort of patients with Becker muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 35474226
- PMCID: PMC9321020
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.27565
Body composition and myokines in a cohort of patients with Becker muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Introduction/aims: Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) is an X-linked disease leading to muscle wasting and weakness. The decrease in lean body mass (LBM) in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, has shown correlation with loss of muscle function and bone density (BD). Myokines (including irisin) are hormones secreted by skeletal muscle that allow crosstalk between muscle and bone. The present study analyzed body composition and circulating myokine levels in a cohort of BMD patients; moreover, the association between dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) parameters, functional motor assessments, and myokine levels was investigated.
Methods: All patients underwent DXA, blood samples for myokine assays, and functional motor assessments. A group of healthy controls (HCs) was also included.
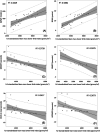
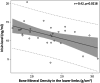
Results: Thirty BMD patients, median age at evaluation 36.0 y [26.0-41.0], were included. Twenty-nine patients underwent whole-body DXA. Median value of total body Z-score was -0.70. The prevalence of low skeletal muscle mass defined as appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMMI) < 7.59 kg/m2 was 83%. Irisin levels were significantly lower in BMD compared to HCs (p = .03). All DXA parameters showed significant correlation with the functional motor assessments, in particular the h2 -standardized lean mass lower limb index (p = .0006); h2 -standardized total fat mass showed negative correlations with North Star Ambulatory Assessment and 6 min walk test (p = .03).
Discussion: DXA is a useful tool to evaluate body composition in BMD patients; the decrease in BD and LBM is associated with a reduction of motor function in BMD.
Keywords: Becker muscular dystrophy; DXA; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; Irisin; bone mineral density.
© 2022 The Authors. Muscle & Nerve published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Appendicular lean mass index and motor function in ambulatory patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Muscle Nerve. 2024 Aug;70(2):226-231. doi: 10.1002/mus.28173. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Muscle Nerve. 2024. PMID: 38837739
-
Appendicular lean mass index changes in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Becker muscular dystrophy.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023 Dec;14(6):2804-2812. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13357. Epub 2023 Oct 25. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023. PMID: 37878526 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in appendicular lean mass in males with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A retrospective review.Muscle Nerve. 2021 Feb;63(2):231-238. doi: 10.1002/mus.27107. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Muscle Nerve. 2021. PMID: 33104257
-
Skeletal health in Duchenne dystrophy: bone-size and subcranial dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry analyses.Muscle Nerve. 2014 Apr;49(4):512-9. doi: 10.1002/mus.23963. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Muscle Nerve. 2014. PMID: 23893858
-
Pharmacology of manipulating lean body mass.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Jan;42(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12320. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25311629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Irisin and Bone in Sickness and in Health: A Narrative Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 21;11(22):6863. doi: 10.3390/jcm11226863. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36431340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Larson CM, Henderson RC. Bone mineral density and fractures in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20(1):71‐74. - PubMed
-
- Palmieri GM, Bertorini TE, Griffin JW, Igarashi M, Karas JG. Assessment of whole body composition with dual energy x‐ray absorptiometry in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: correlation of lean body mass with muscle function. Muscle Nerve. 1996;19(6):777‐779. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199606)19:6<777::AID-MUS15>3.0.CO;2-I - DOI - PubMed

