A novel SCARECROW-LIKE3 transcription factor LjGRAS36 in Lotus japonicus regulates the development of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis
- PMID: 35465207
- PMCID: PMC8986927
- DOI: 10.1007/s12298-022-01161-z
A novel SCARECROW-LIKE3 transcription factor LjGRAS36 in Lotus japonicus regulates the development of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis
Abstract
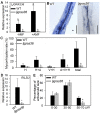
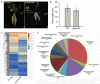
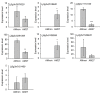
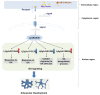
The symbiosis with arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi improves plants' nutrient uptake. During this process, transcription factors have been highlighted to play crucial roles. Members of the GRAS transcription factor gene family have been reported involved in AM symbiosis, but little is known about SCARECROW-LIKE3 (SCL3) genes belonging to this family in Lotus japonicus. In this study, 67 LjGRAS genes were identified from the L. japonicus genome, seven of which were clustered in the SCL3 group. Three of the seven LjGRAS genes expression levels were upregulated by AM fungal inoculation, and our biochemical results showed that the expression of LjGRAS36 was specifically induced by AM colonization. Functional loss of LjGRAS36 in mutant ljgras36 plants exhibited a significantly reduced mycorrhizal colonization rate and arbuscular size. Transcriptome analysis showed a deficiency of LjGRAS36 led to the dysregulation of the gibberellic acid signal pathway associated with AM symbiosis. Together, this study provides important insights for understanding the important potential function of SCL3 genes in regulating AM symbiotic development.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12298-022-01161-z.
Keywords: Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; Gibberellic acid signal pathway; Lotus japonicus; SCL3; Symbiosis.
© Prof. H.S. Srivastava Foundation for Science and Society 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysfunction in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis has consistent but small effects on the establishment of the fungal microbiota in Lotus japonicus.New Phytol. 2019 Oct;224(1):409-420. doi: 10.1111/nph.15958. Epub 2019 Jul 2. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 31125425 Free PMC article.
-
Network of GRAS transcription factors involved in the control of arbuscule development in Lotus japonicus.Plant Physiol. 2015 Mar;167(3):854-71. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.255430. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25560877 Free PMC article.
-
ARBUSCULAR MYCORRHIZA-INDUCED KINASES AMK8 and AMK24 associate with the receptor-like kinase KINASE3 to regulate arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in Lotus japonicus.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):2006-2026. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad050. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36808553 Free PMC article.
-
Multifarious and Interactive Roles of GRAS Transcription Factors During Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Development.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 28;13:836213. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.836213. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35419017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the dialogue between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and polyamines in plants.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jul 14;38(9):159. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03336-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35834138 Review.
Cited by
-
MyC Factor Analogue CO5 Promotes the Growth of Lotus japonicus and Enhances Stress Resistance by Activating the Expression of Relevant Genes.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;10(7):458. doi: 10.3390/jof10070458. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartoli B, Bernardini P, Bi XJ, Bolognino I, Branchini P, Budano A, Melcarne AKC, Camarri P, Cao Z, Cardarelli R, Catalanotti S, Cattaneo C, Chen SZ, Chen TL, Chen Y, Creti P, Cui SW, Dai BZ, Staiti GD, D’Amone A, De Danzengluobu I, Piazzoli BD, Di Girolamo T, Ding XH, Di Sciascio G, Feng CF, Feng ZY, Feng ZY, Galeazzi F, Giroletti E, Gou QB, Guo YQ, He HH, Hu HB, Hu HB, Huang Q, Iacovacci M, Iuppa R, James I, Jia HY, Labaciren, Li HJ, Li JY, Li XX, Liguori G, Liu C, Liu CQ, Liu J, Liu MY, Lu H, Ma LL, Ma XH, Mancarella G, Mari SM, Marsella G, Martello D, Mastroianni S, Montini P, Ning CC, Pagliaro A, Panareo M, Panico B, Perrone L, Pistilli P, Ruggieri F, Salvini P, Santonico R, Sbano SN, Shen PR, Sheng XD, Shi F, Surdo A, Tan YH, Vallania P, Vernetto S, Vigorito C, Wang B, Wang H, Wu CY, Wu HR, Xu B, Xue L, Yang QY, Yang XC, Yao ZG, Yuan AF, Zha M, Zhang HM, Zhang JL, Zhang JL, Zhang L, Zhang P, Zhang XY, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Zhaxiciren XX, Zhu FR, Zhu QQ, Zizzi G, Collaboration (2013) A-Y Observation of TeV gamma rays from the unidentified source HESS J1841-055 with the ARGO-YBJ Experiment. Astrophys J767: 99
-
- Bolle C. The role of GRAS proteins in plant signal transduction and development. Planta. 2004;218:683–692. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Jin W, Liu A, Zhang S, Liu D, Wang F, Lin X, He C. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) increase growth and secondary metabolism in cucumber subjected to low temperature stress. Sci Hort. 2013;160:222–229.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
