A Modified Fibronectin Type III Domain-Conjugated, Long-Acting Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitor with Extended Half-Life
- PMID: 35458385
- PMCID: PMC9028128
- DOI: 10.3390/v14040655
A Modified Fibronectin Type III Domain-Conjugated, Long-Acting Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitor with Extended Half-Life
Abstract
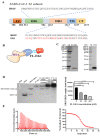
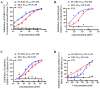
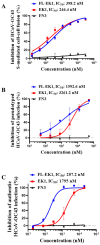
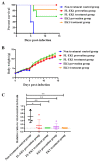
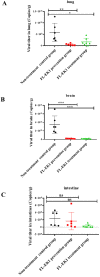
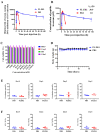
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by infection of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants has posed serious threats to global public health, thus calling for the development of potent and broad-spectrum antivirals. We previously designed and developed a peptide-based pan-coronavirus (CoV) fusion inhibitor, EK1, which is effective against all human CoVs (HCoV) tested by targeting the HCoV S protein HR1 domain. However, its relatively short half-life may limit its clinical use. Therefore, we designed, constructed, and expressed a recombinant protein, FL-EK1, which consists of a modified fibronectin type III domain (FN3) with albumin-binding capacity, a flexible linker, and EK1. As with EK1, we found that FL-EK1 could also effectively inhibit infection of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, as well as HCoV-OC43. Furthermore, it protected mice from infection by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant and HCoV-OC43. Importantly, the half-life of FL-EK1 (30 h) is about 15.7-fold longer than that of EK1 (1.8 h). These results suggest that FL-EK1 is a promising candidate for the development of a pan-CoV fusion inhibitor-based long-acting antiviral drug for preventing and treating infection by current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants, as well as other HCoVs.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; albumin; fusion inhibitor; human coronavirus; long-acting.
Conflict of interest statement
S.J., L.L., S.X., W.X., Q.W., Q.D. and R.W. are the inventors in the patent or patent application covering the peptides EK1 and FL- EK1. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus infectious diseases.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28143. Epub 2022 Sep 22. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36098460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting the HR1 domain of human coronavirus spike.Sci Adv. 2019 Apr 10;5(4):eaav4580. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4580. eCollection 2019 Apr. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 30989115 Free PMC article.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol-Conjugated EK1 Peptide with Potent and Broad-Spectrum Inhibitory Activity against SARS-CoV-2, Its Variants of Concern, and Other Human Coronaviruses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 1;22(21):11869. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111869. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769299 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion.Cell Res. 2020 Apr;30(4):343-355. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0305-x. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32231345 Free PMC article.
-
Human coronaviruses and therapeutic drug discovery.Infect Dis Poverty. 2021 Mar 16;10(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00812-9. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021. PMID: 33726861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IgG Fc-Binding Peptide-Conjugated Pan-CoV Fusion Inhibitor Exhibits Extended In Vivo Half-Life and Synergistic Antiviral Effect When Combined with Neutralizing Antibodies.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 22;13(9):1283. doi: 10.3390/biom13091283. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759683 Free PMC article.
-
Targetable elements in SARS-CoV-2 S2 subunit for the design of pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors and vaccines.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 10;8(1):197. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01472-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37164987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus infectious diseases.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28143. Epub 2022 Sep 22. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36098460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FEOpti-ACVP: identification of novel anti-coronavirus peptide sequences based on feature engineering and optimization.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):bbae037. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae037. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38366802 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Proteome Signatures of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinated Healthcare Workers in Greece Associated with Their Prior Infection Status.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 5;23(17):10153. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710153. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woo P.C., Lau S.K., Lam C.S., Lau C.C., Tsang A.K., Lau J.H., Bai R., Teng J.L., Tsang C.C., Wang M., et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012;86:3995–4008. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06540-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pascarella S., Ciccozzi M., Zella D., Bianchi M., Benedetti F., Benvenuto D., Broccolo F., Cauda R., Caruso A., Angeletti S., et al. SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 Indian variants: Are electrostatic potential changes responsible for a higher transmission rate? J. Med. Virol. 2021;93:6551–6556. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27210. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

