Inhibition of RhoA and Cdc42 by miR-133a Modulates Retinoic Acid Signalling during Early Development of Posterior Cardiac Tube Segment
- PMID: 35456995
- PMCID: PMC9025022
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23084179
Inhibition of RhoA and Cdc42 by miR-133a Modulates Retinoic Acid Signalling during Early Development of Posterior Cardiac Tube Segment
Abstract
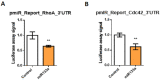
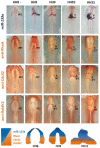
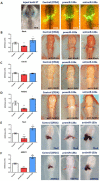
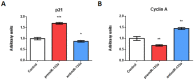
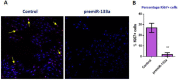
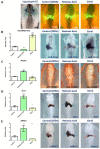
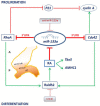
It is well known that multiple microRNAs play crucial roles in cardiovascular development, including miR-133a. Additionally, retinoic acid regulates atrial marker expression. In order to analyse the role of miR-133a as a modulator of retinoic acid signalling during the posterior segment of heart tube formation, we performed functional experiments with miR-133a and retinoic acid by means of microinjections into the posterior cardiac precursors of both primitive endocardial tubes in chick embryos. Subsequently, we subjected embryos to whole mount in situ hybridisation, immunohistochemistry and qPCR analysis. Our results demonstrate that miR-133a represses RhoA and Cdc42, as well as Raldh2/Aldh1a2, and the specific atrial markers Tbx5 and AMHC1, which play a key role during differentiation. Furthermore, we observed that miR-133a upregulates p21 and downregulates cyclin A by repressing RhoA and Cdc42, respectively, thus functioning as a cell proliferation inhibitor. Additionally, retinoic acid represses miR-133a, while it increases Raldh2, Tbx5 and AMHC1. Given that RhoA and Cdc42 are involved in Raldh2 expression and that they are modulated by miR-133a, which is influenced by retinoic acid signalling, our results suggest the presence of a negative feedback mechanism between miR-133a and retinoic acid during early development of the posterior cardiac tube segment. Despite additional unexplored factors being possible contributors to this negative feedback mechanism, miR-133a might also be considered as a potential therapeutic tool for the diagnosis, therapy and prognosis of cardiac diseases.
Keywords: Cdc42; Raldh2; RhoA; atrial differentiation; cardiac development; miR-133a; retinoic acid signalling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-1 as a Key Epigenetic Regulator in Early Differentiation of Cardiac Sinoatrial Region.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 15;25(12):6608. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126608. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928314 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase is expressed during early heart development and is required for cardiac chamber formation.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Oct 1;88(1):111-20. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq179. Epub 2010 Jun 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20525643
-
Sequential programs of retinoic acid synthesis in the myocardial and epicardial layers of the developing avian heart.Dev Biol. 2000 Mar 1;219(1):129-41. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9588. Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10677260
-
MicroRNAs and their therapeutic potential for human diseases: MiR-133a and bronchial smooth muscle hyperresponsiveness in asthma.J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;114(3):264-8. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10r10fm. Epub 2010 Oct 9. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20953121 Review.
-
miR-133a-A Potential Target for Improving Cardiac Mitochondrial Health and Regeneration After Injury.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 1;80(2):187-193. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001279. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35500168 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Non-Coding RNA Transcriptomics in Heart Failure.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 30;10(12):3076. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123076. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA H19 Impairs Chemo and Radiotherapy in Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 27;23(15):8309. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158309. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-1 as a Key Epigenetic Regulator in Early Differentiation of Cardiac Sinoatrial Region.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 15;25(12):6608. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126608. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928314 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs as Key Regulators for Cardiac Development and Cardiovascular Diseases.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Apr 12;10(4):166. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10040166. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37103045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lopez-Sanchez C., Garcia-Martinez V., Schoenwolf G.C. Localization of cells of the prospective neural plate, heart and somites within the primitive streak and epiblast of avian embryos at intermediate primitive-streak Stages. Cells Tissues Organs. 2001;169:334–346. doi: 10.1159/000047900. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

