Calpains as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Myocardial Hypertrophy
- PMID: 35456920
- PMCID: PMC9032729
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23084103
Calpains as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Myocardial Hypertrophy
Abstract
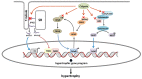
Despite advances in its treatment, heart failure remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality, evidencing an urgent need for novel mechanism-based targets and strategies. Myocardial hypertrophy, caused by a wide variety of chronic stress stimuli, represents an independent risk factor for the development of heart failure, and its prevention constitutes a clinical objective. Recent studies performed in preclinical animal models support the contribution of the Ca2+-dependent cysteine proteases calpains in regulating the hypertrophic process and highlight the feasibility of their long-term inhibition as a pharmacological strategy. In this review, we discuss the existing evidence implicating calpains in the development of cardiac hypertrophy, as well as the latest advances in unraveling the underlying mechanisms. Finally, we provide an updated overview of calpain inhibitors that have been explored in preclinical models of cardiac hypertrophy and the progress made in developing new compounds that may serve for testing the efficacy of calpain inhibition in the treatment of pathological cardiac hypertrophy.
Keywords: calpain; calpastatin; heart failure; myocardial hypertrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calpains mediate isoproterenol-induced hypertrophy through modulation of GRK2.Basic Res Cardiol. 2019 Mar 26;114(3):21. doi: 10.1007/s00395-019-0730-5. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30915659
-
Calpain-dependent cleavage of N-cadherin is involved in the progression of post-myocardial infarction remodeling.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 11;289(28):19408-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.567206. Epub 2014 Jun 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24891510 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the calpain/calpastatin system as a new strategy to prevent cardiovascular remodeling in angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Circ Res. 2008 Mar 28;102(6):720-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.160077. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18258859
-
The role of calpains in myocardial remodelling and heart failure.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Oct 1;96(1):38-45. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs099. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22425901 Review.
-
Tear me down: role of calpain in the development of cardiac ventricular hypertrophy.Circ Res. 2011 Aug 5;109(4):453-62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.239749. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21817165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of calpastatin hcast 3-25 and activity of the calpain/calpastatin system in human glioblastoma stem cells: possible involvement of hcast 3-25 in cell differentiation.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jul 30;11:1359956. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1359956. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39139809 Free PMC article.
-
Role and molecular mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitors in pathological cardiac remodeling (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 May;29(5):73. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13197. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38488029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of a cysteine protease inhibitor compared with enalapril in murine heart failure models.iScience. 2024 Sep 11;27(10):110935. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110935. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39381741 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

