Wettability and Surface Roughness Analysis of Laser Surface Texturing of AISI 430 Stainless Steel
- PMID: 35454645
- PMCID: PMC9028002
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15082955
Wettability and Surface Roughness Analysis of Laser Surface Texturing of AISI 430 Stainless Steel
Abstract
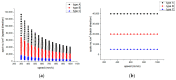
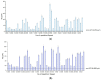
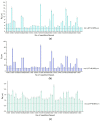
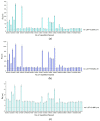
Due to its wide applicability in industry, devising microstructures on the surface of materials can be easily implemented and automated in technological processes. Laser Surface Texturing (LST) is applied to modify the chemical composition, morphology, and roughness of surfaces (wettability), cleaning (remove contaminants), reducing internal stresses of metals (hardening, tempering), surface energy (polymers, metals), increasing the adhesion (hybrid joining, bioengineering) and decreasing the growth of pathogenic bacteria (bioengineering). This paper is a continuation and extension of our previous studies in laser-assisted texturing of surfaces. Three different patterns (crater array-type C, two ellipses at 90° overlapping with its mirror-type B and 3 concentric octagons-type A) were applied with a nanosecond pulsed laser (active medium Nd: Fiber Diode-pumped) on the surface of a ferritic stainless steel (AISI 430). Micro texturing the surface of a material can modify its wettability behavior. A hydrophobic surface (contact angle greater than 90°) was obtained with different variations depending on the parameters. The analysis performed in this research (surface roughness, wettability) is critical for assessing the surface functionality, characteristics and properties of the stainless steel surface after the LST process. The values of the surface roughness and the contact angle are directly proportional to the number of repetitions and inversely proportional to the speed. Recommendations for the use of different texturing pattern designs are also made.
Keywords: ferritic stainless steel; surface laser texturing; surface patterning; surface roughness; wettability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




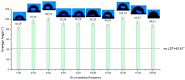
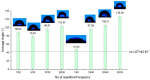
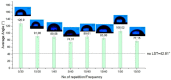
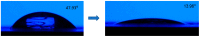

Similar articles
-
Morphological Analysis of Laser Surface Texturing Effect on AISI 430 Stainless Steel.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;15(13):4580. doi: 10.3390/ma15134580. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35806705 Free PMC article.
-
Wettability and friction control of a stainless steel surface by combining nanosecond laser texturing and adsorption of superhydrophobic nanosilica particles.Sci Rep. 2018 May 10;8(1):7457. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25850-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29748545 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Surfaces with Persistent Antimicrobial Properties on Stainless Steel Developed Using Femtosecond Laser Texturing for Application in "High Traffic" Objects.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Aug 23;13(17):2396. doi: 10.3390/nano13172396. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37686904 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Surface Nano-Roughness on the Wettability Performance of Microstructured Metallic Surface Using Direct Laser Interference Patterning.Materials (Basel). 2019 Aug 27;12(17):2737. doi: 10.3390/ma12172737. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31461830 Free PMC article.
-
Surface modification of zirconia or lithium disilicate-reinforced glass ceramic by laser texturing to increase the adhesion of prosthetic surfaces to resin cements: an integrative review.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Jul;27(7):3331-3345. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05016-z. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37069409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Different Laser Groove Texture Collation Frequency on Tribological Properties of 0Cr17Ni7Al Stainless Steel.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jun 22;15(13):4419. doi: 10.3390/ma15134419. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35806542 Free PMC article.
-
Wetting Behavior Driven by Surface Morphology Changes Induced by Picosecond Laser Texturing.Materials (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;17(8):1719. doi: 10.3390/ma17081719. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38673077 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological Analysis of Laser Surface Texturing Effect on AISI 430 Stainless Steel.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;15(13):4580. doi: 10.3390/ma15134580. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35806705 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Surface Treatment Degree of Steel Sheets in the Bonding Process.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;15(15):5158. doi: 10.3390/ma15155158. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35897588 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the Role of Oxygen in Obtaining Long-Term Stable Superhydrophilic Surfaces on Metals Treated with a Femtosecond Laser.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 5;8(37):33904-33911. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04618. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37744860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimamoto K., Sekiguchi Y., Sato C. Effects of surface treatment on the critical energy release rates of welded joints between glass fiber reinforced polypropylene and a metal. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016;67:31–37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2015.12.022. - DOI
-
- Setti D., Arrabiyeh P.A., Kirsch B., Heintz M., Aurich J.C. Analytical and experimental investigations on the mechanisms of surface generation in micro grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020;149:103489. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.103489. - DOI
-
- Salstela J., Suvanto M., Pakkanen T.T. Influence of hierarchical micro-micro patterning and chemical modifications on adhesion between aluminum and epoxy. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016;66:128–137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2015.12.036. - DOI
-
- Xu H., Cong W., Yang D., Ma Y., Zhong W., Tan P., Yan J. Microstructure and mechanical performance of dissimilar metal joints of aluminium alloy and stainless steel by cutting-assisted welding-brazing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. 2022;119:4411–4421. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-08452-x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

