Identification of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Regions in a Non-Model Insect Species Ostrinia nubilalis (Hbn.)
- PMID: 35454181
- PMCID: PMC9029825
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12040592
Identification of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Regions in a Non-Model Insect Species Ostrinia nubilalis (Hbn.)
Abstract
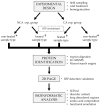
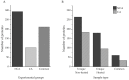
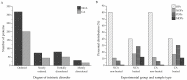
Research in previous decades has shown that intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) and regions in proteins (IDRs) are as ubiquitous as highly ordered proteins. Despite this, research on IDPs and IDRs still has many gaps left to fill. Here, we present an approach that combines wet lab methods with bioinformatics tools to identify and analyze intrinsically disordered proteins in a non-model insect species that is cold-hardy. Due to their known resilience to the effects of extreme temperatures, these proteins likely play important roles in this insect's adaptive mechanisms to sub-zero temperatures. The approach involves IDP enrichment by sample heating and double-digestion of proteins, followed by peptide and protein identification. Next, proteins are bioinformatically analyzed for disorder content, presence of long disordered regions, amino acid composition, and processes they are involved in. Finally, IDP detection is validated with an in-house 2D PAGE. In total, 608 unique proteins were identified, with 39 being mostly disordered, 100 partially disordered, 95 nearly ordered, and 374 ordered. One-third contain at least one long disordered segment. Functional information was available for only 90 proteins with intrinsic disorders out of 312 characterized proteins. Around half of the 90 proteins are cytoskeletal elements or involved in translational processes.
Keywords: IUPred analysis; LC–MS/MS; Ostrinia nubilalis; cold hardiness; intrinsically disordered protein regions (IDRs); intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
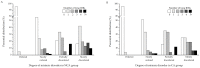
Similar articles
-
Archaic chaos: intrinsically disordered proteins in Archaea.BMC Syst Biol. 2010 May 28;4 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-S1-S1. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 20522251 Free PMC article.
-
Do sequence neighbours of intrinsically disordered regions promote structural flexibility in intrinsically disordered proteins?J Struct Biol. 2020 Feb 1;209(2):107428. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2019.107428. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 31756456
-
Analyzing IDPs in Interactomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2141:895-945. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0524-0_46. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32696395
-
Advantages of proteins being disordered.Protein Sci. 2014 May;23(5):539-50. doi: 10.1002/pro.2443. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24532081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional unfoldomics: Roles of intrinsic disorder in protein (multi)functionality.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2024;138:179-210. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2023.11.001. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38220424 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of inorganic elements by overwintering physiology of cold hardy larvae of European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis, Hbn.).J Comp Physiol B. 2024 Apr;194(2):145-154. doi: 10.1007/s00360-024-01537-5. Epub 2024 Mar 13. J Comp Physiol B. 2024. PMID: 38478065
-
Characterization of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins in Healthy and Diseased States by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2024;19(3):176-188. doi: 10.2174/0115748871271420240213064251. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2024. PMID: 38409704 Review.
-
Per Aspera ad Chaos: Vladimir Uversky's Odyssey through the Strange World of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 19;13(6):1015. doi: 10.3390/biom13061015. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

