TXNIP: A Double-Edged Sword in Disease and Therapeutic Outlook
- PMID: 35450411
- PMCID: PMC9017576
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7805115
TXNIP: A Double-Edged Sword in Disease and Therapeutic Outlook
Abstract
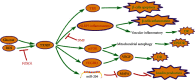
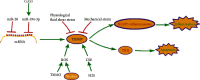
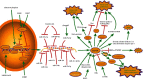
Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) was originally named vitamin D3 upregulated protein-1 (VDUP1) because of its ability to bind to thioredoxin (TRX) and inhibit TRX function and expression. TXNIP is an alpha-arrestin protein that is essential for redox homeostasis in the human body. TXNIP may act as a double-edged sword in the cell. The balance of TXNIP is crucial. A study has shown that TXNIP can travel between diverse intracellular locations and bind to different proteins to play different roles under oxidative stress. The primary function of TXNIP is to induce apoptosis or pyroptosis under oxidative stress. TXNIP also inhibits proliferation and migration in cancer cells, although TXNIP levels decrease, and function diminishes in various cancers. In this review, we summarized the main structure, binding proteins, pathways, and the role of TXNIP in diseases, aiming to explore the double-edged sword role of TXNIP, and expect it to be helpful for future treatment using TXNIP as a therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2022 Min Pan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin interacting protein: redox dependent and independent regulatory mechanisms.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Mar 15;16(6):587-96. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4137. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 21929372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structural basis for the negative regulation of thioredoxin by thioredoxin-interacting protein.Nat Commun. 2014;5:2958. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3958. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24389582 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-oxidative, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory actions by thioredoxin 1 and thioredoxin-binding protein-2.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Sep;127(3):261-70. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 8. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20435060 Review.
-
Roles of thioredoxin binding protein (TXNIP) in oxidative stress, apoptosis and cancer.Mitochondrion. 2013 May;13(3):163-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Mitochondrion. 2013. PMID: 22750447 Review.
-
Nitrosative/oxidative stress conditions regulate thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) expression and thioredoxin-1 (TRX-1) nuclear localization.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e84588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084588. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376827 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory Role of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein in Cancer's Impediments: Current Understanding and Therapeutic Implications.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;10(11):1902. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111902. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-Denitrosylation: A Crosstalk between Glutathione and Redoxin Systems.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;11(10):1921. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101921. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Role of Selenoprotein M.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;12(11):1906. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111906. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD69 serves as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 May 8;13(1):7452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34261-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37156819 Free PMC article.
-
TXNIP: A key protein in the cellular stress response pathway and a potential therapeutic target.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Jul;55(7):1348-1356. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01019-8. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37394581 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen K. S., DeLuca H. F. Isolation and characterization of a novel cDNA from HL-60 cells treated with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta . 1994;1219(1):26–32. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama A., Matsui M., Iwata S., et al. Identification of thioredoxin-binding protein-2/vitamin D(3) up-regulated protein 1 as a negative regulator of thioredoxin function and expression. The Journal of Biological Chemistry . 1999;274(31):21645–21650. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig D. L., Kotanides H., Le T., Chavkin D., Bohlen P., Witte L. Cloning, genetic characterization, and chromosomal mapping of the mouse VDUP1 gene. Gene . 2001;269(1-2):103–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

