HLA-A2 Promotes the Therapeutic Effect of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Hyperoxic Lung Injury
- PMID: 35447737
- PMCID: PMC9029550
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9040177
HLA-A2 Promotes the Therapeutic Effect of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Hyperoxic Lung Injury
Abstract
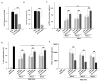
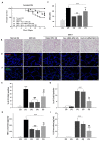
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are one of the most extensively studied stem cell types owing to their capacity for differentiation into multiple lineages as well as their ability to secrete regenerative factors and modulate immune functions. However, issues remain regarding their further application for cell therapy. Here, to demonstrate the superiority of the improvement of MSCs, we divided umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs (UCB-MSCs) from 15 donors into two groups based on efficacy and revealed donor-dependent variations in the anti-inflammatory effect of MSCs on macrophages as well as their immunoregulatory effect on T cells. Through surface marker analyses (242 antibodies), we found that HLA-A2 was positively related to the anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory function of MSCs. Additionally, HLA-A2 mRNA silencing in MSCs attenuated their therapeutic effects in vitro; namely, the suppression of LPS-stimulated macrophages and phytohemagglutinin-stimulated T cells. Moreover, HLA-A2 silencing in MSCs significantly decreased their therapeutic effects in a rat model of hyperoxic lung damage. The present study provides novel insights into the quality control of donor-derived MSCs for the treatment of inflammatory conditions and diseases.
Keywords: HLA-A2; T cell suppression; UCB-MSCs; anti-inflammation; hyperoxic lung damage; quality control; surface maker array.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble PTX3 of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuates Hyperoxic Lung Injury by Activating Macrophage Polarization in Neonatal Rat Model.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Jan 23;2020:1802976. doi: 10.1155/2020/1802976. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32399038 Free PMC article.
-
Decorin Secreted by Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induces Macrophage Polarization via CD44 to Repair Hyperoxic Lung Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 27;20(19):4815. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194815. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31569732 Free PMC article.
-
[IMMUNOGENICITY OF HUMAN UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD DERIVED MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS AFTER OSTEOGENIC INDUCTION].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;28(6):752-7. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 26455231 Chinese.
-
Current Status of Canine Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Veterinary Medicine.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jul 15;2018:8329174. doi: 10.1155/2018/8329174. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30123294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What is the impact of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on clinical treatment?Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Dec 1;11(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02011-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33261658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee M., Jeong S.Y., Ha J., Kim M., Jin H.J., Kwon S.J., Chang J.W., Choi S.J., Oh W., Yang Y.S., et al. Low immunogenicity of allogeneic human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014;446:983–989. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.03.051. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

