TRPM2 deficiency in mice protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting TRPM2-CD36 inflammatory axis in macrophages
- PMID: 35445217
- PMCID: PMC9015693
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-022-00027-7
TRPM2 deficiency in mice protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting TRPM2-CD36 inflammatory axis in macrophages
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: TRPM2 deficiency in mice protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting TRPM2-CD36 inflammatory axis in macrophages.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Jul;2(7):703. doi: 10.1038/s44161-023-00303-0. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 39195930 No abstract available.
-
Publisher Correction: RPM2 deficiency in mice protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting TRPM2-CD36 inflammatory axis in macrophages.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Apr;1(4):402. doi: 10.1038/s44161-022-00059-z. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 39196136 No abstract available.
-
Author Correction: TRPM2 deficiency in mice protects against atherosclerosis by inhibiting TRPM2-CD36 inflammatory axis in macrophages.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Apr;1(4):401. doi: 10.1038/s44161-022-00062-4. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 39196137 No abstract available.
Abstract
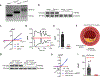
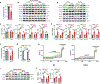
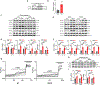
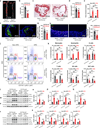
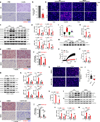
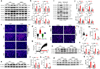
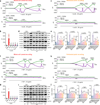
Atherosclerosis is the major cause of ischemic heart disease and stroke, the leading causes of mortality worldwide. The central pathological features of atherosclerosis include macrophage infiltration and foam cell formation. However, the detailed mechanisms regulating these two processes remain unclear. Here we show that oxidative stress-activated Ca2+-permeable transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) plays a critical role in atherogenesis. Both global and macrophage-specific Trpm2 deletion protect Apoe -/- mice against atherosclerosis. Trpm2 deficiency reduces oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) uptake by macrophages, thereby minimizing macrophage infiltration, foam cell formation and inflammatory responses. Activation of the oxLDL receptor CD36 induces TRPM2 activity, and vice versa. In cultured macrophages, TRPM2 is activated by CD36 ligands oxLDL and thrombospondin-1 (TSP1), and deleting Trpm2 or inhibiting TRPM2 activity suppresses the activation of CD36 signaling cascade induced by oxLDL and TSP1. Our findings establish the TRPM2-CD36 axis as a molecular mechanism underlying atherogenesis, and suggest TRPM2 as a potential therapeutic target for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; CD36; Ca2+ signaling; TRPM2; TSP1; macrophages; oxLDL.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
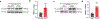


Similar articles
-
Activation of endothelial TRPM2 exacerbates blood-brain barrier degradation in ischemic stroke.Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Mar 13;120(2):188-202. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad126. Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 37595268 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV4 calcium-permeable channel is a novel regulator of oxidized LDL-induced macrophage foam cell formation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Sep;110:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28602913
-
Nicotine potentiates proatherogenic effects of oxLDL by stimulating and upregulating macrophage CD36 signaling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Aug 15;305(4):H563-74. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00042.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23748423 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized LDL-bound CD36 recruits an Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase-Lyn complex in macrophages that promotes atherosclerosis.Sci Signal. 2015 Sep 8;8(393):ra91. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa9623. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26350901 Free PMC article.
-
CD36, a scavenger receptor implicated in atherosclerosis.Exp Mol Med. 2014 Jun 6;46(6):e99. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.38. Exp Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24903227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Volatilome is Inflammasome- and Lipidome-dependent in Ischemic Heart Disease.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2024;20(6):e190724232038. doi: 10.2174/011573403X302934240715113647. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39039680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRP Ion Channels in Immune Cells and Their Implications for Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 27;25(5):2719. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052719. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles with platelet membrane fusion for targeted therapy of atherosclerosis.Bioact Mater. 2024 Feb 17;35:447-460. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.015. eCollection 2024 May. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38390527 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 induced TRPM2 mediated neuropathic pain.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 12;15:1472771. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1472771. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39329114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contribution of ion channels to shaping macrophage behaviour.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 7;13:970234. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.970234. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
