An emerging class of new therapeutics targeting TGF, Activin, and BMP ligands in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 35434863
- PMCID: PMC10952790
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.478
An emerging class of new therapeutics targeting TGF, Activin, and BMP ligands in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
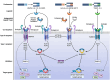
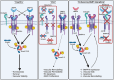
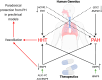
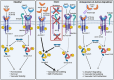
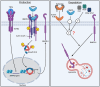
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is an often fatal condition, the primary pathology of which involves loss of pulmonary vascular perfusion due to progressive aberrant vessel remodeling. The reduced capacity of the pulmonary circulation places increasing strain on the right ventricle of the heart, leading to death by heart failure. Currently, licensed therapies are primarily vasodilators, which have increased the median post-diagnosis life expectancy from 2.8 to 7 years. Although this represents a substantial improvement, the search continues for transformative therapeutics that reverse established disease. The genetics of human PAH heavily implicates reduced endothelial bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling as a causal role for the disease pathobiology. Recent approaches have focused on directly enhancing BMP signaling or removing the inhibitory influence of pathways that repress BMP signaling. In this critical commentary, we review the evidence underpinning the development of two approaches: BMP-based agonists and inhibition of activin/GDF signaling. We also address the key considerations and questions that remain regarding these approaches.
© 2022 The Authors. Developmental Dynamics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for Anatomy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of the bone morphogenetic protein system in endothelin- and aldosterone-induced cell proliferation of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells isolated from human patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Hypertens Res. 2010 May;33(5):435-45. doi: 10.1038/hr.2010.16. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Hypertens Res. 2010. PMID: 20186146
-
Altered bone morphogenetic protein and transforming growth factor-beta signaling in rat models of pulmonary hypertension: potential for activin receptor-like kinase-5 inhibition in prevention and progression of disease.Circulation. 2009 Feb 3;119(4):566-76. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.821504. Epub 2009 Jan 19. Circulation. 2009. PMID: 19153267
-
Autophagy contributes to BMP type 2 receptor degradation and development of pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Pathol. 2019 Nov;249(3):356-367. doi: 10.1002/path.5322. Epub 2019 Aug 27. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31257577 Free PMC article.
-
BMP type II receptor as a therapeutic target in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Aug;74(16):2979-2995. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2510-4. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28447104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relevant issues in the pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Dec 24;62(25 Suppl):D4-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.025. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24355640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025 Feb;22(2):105-120. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01064-4. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39112561 Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signalling in pulmonary arterial hypertension: revisiting the BMPRII connection.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Jun 26;52(3):1515-1528. doi: 10.1042/BST20231547. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38716930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex-biased TGFβ signalling in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Oct 24;119(13):2262-2277. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad129. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 37595264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Context-dependent TGFβ family signalling in cell fate regulation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Dec;24(12):876-894. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00638-3. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37596501 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FS/SBSRF/20/31005/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RG/19/3/34265/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CH/09/001/25945/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/17/58/33134/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/17/1/32532/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

