SARS-CoV-2 and neurodegenerative diseases: what we know and what we don't
- PMID: 35434769
- PMCID: PMC9013492
- DOI: 10.1007/s00702-022-02500-w
SARS-CoV-2 and neurodegenerative diseases: what we know and what we don't
Abstract
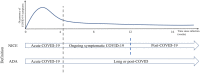
Infection of the CNS with the SARS-CoV-2 can occur via different routes and results in para- or post-infectious manifestations with a variety of neurological symptoms. In patients with neurodegenerative diseases, SARS-CoV-2 is often associated with a higher fatality rate, which is a relevant problem in increasingly older populations. Apart from the direct consequences of an infection in patients with neurodegenerative diseases, indirect consequences of the pandemic such as limited access to care facilities and treatment have negative effects on the course of these chronic disorders. The occurrence of long-lasting neurological symptoms after infection with SARS-CoV-2 indicates a prolonged impact on the CNS. However, while it is known that SARS-CoV-2 affects neuronal populations that are relevant in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, it is yet unclear whether an infection with SARS-CoV-2 is sufficient to trigger neurodegeneration. Reflecting on the impact of SARS-CoV-2 on neurodegeneration, we provide a concise overview on the current knowledge of SARS-CoV-2-induced pathology in the CNS and discuss yet open questions in the field.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; COVID-19; Neurodegeneration; Neurological symptoms; Parkinson’s disease; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests related to this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging COVID-19 Neurological Manifestations: Present Outlook and Potential Neurological Challenges in COVID-19 Pandemic.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Sep;58(9):4694-4715. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02450-6. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34169443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and neurological disorders: are neurodegenerative or neuroimmunological diseases more vulnerable?J Neurol. 2021 Feb;268(2):409-419. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10070-8. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 32696341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Pathogenicity on the Central Nervous System: Bridging Experimental Probes to Clinical Evidence and Therapeutic Interventions.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1376:1-27. doi: 10.1007/5584_2021_675. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 34735712 Review.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Chronic Neurological Disorders: Focus on Patients with Dementia.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022;21(10):1017-1026. doi: 10.2174/1871527321666220111124928. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 35021982 Review.
-
Biomedical Perspectives of Acute and Chronic Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Sequelae of COVID-19.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(6):1229-1240. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666211223130228. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34951387 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2, long COVID, prion disease and neurodegeneration.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 27;16:1002770. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1002770. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36238082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Does the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Hamper the Amyloid Transformation of Alpha-Synuclein after All?Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 9;11(2):498. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020498. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831034 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Neuroinvasion, Inflammatory Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 17;16:937961. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.937961. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35783095 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Neurodegenerative Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Feb 21;12(3):222. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12030222. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The heterogeneity of Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023 Jun;130(6):827-838. doi: 10.1007/s00702-023-02635-4. Epub 2023 May 11. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023. PMID: 37169935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aamodt AH, Hogestol EA, Popperud TH, Holter JC, Dyrhol-Riise AM, Tonby K, Stiksrud B, Quist-Paulsen E, Berge T, Barratt-Due A, Aukrust P, Heggelund L, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Harbo HF. Blood neurofilament light concentration at admittance: a potential prognostic marker in COVID-19. J Neurol. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10517-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ababneh NA, Scaber J, Flynn R, Douglas A, Barbagallo P, Candalija A, Turner MR, Sims D, Dafinca R, Cowley SA, Talbot K. Correction of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis related phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons carrying a hexanucleotide expansion mutation in C9orf72 by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing using homology-directed repair. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(13):2200–2217. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

