Identification of Natural Products as SENP2 Inhibitors for Targeted Therapy in Heart Failure
- PMID: 35431915
- PMCID: PMC9012495
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.817990
Identification of Natural Products as SENP2 Inhibitors for Targeted Therapy in Heart Failure
Abstract
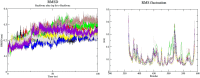
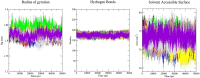
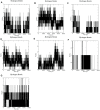
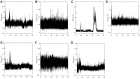
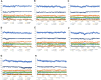
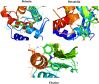
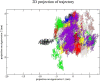
Aims: Sentrin-specific protease -2 (SENP2) is involved in deSUMOylation. Increased deSUMOylation in murine hearts by SENP2 upregulation resulted in cardiac dysfunction and congenital heart defects. Natural compounds via regulating cell proliferation and survival, induce cell cycle cessation, cell death, apoptosis, and producing reactive oxygen species and various enzyme systems cause disease prevention. Then, natural compounds can be suitable inhibitors and since SENP2 is a protein involved in heart disease, so our aim was inhibition of SENP2 by natural products for heart disease treatment. Material and methods: Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation of natural products i.e. Gallic acid (GA), Caffeic acid (CA), Thymoquinone (TQ), Betanin, Betanidin, Fisetin, and Ebselen were done to evaluate the SENP2 inhibitory effect of these natural products. The toxicity of compounds was also predicted. Results: The results showed that Betanin constituted a stable complex with SENP2 active site as it revealed low RMSD, high binding energy, and hydrogen bonds. Further, as compared to Ebselen, Betanin demonstrated low toxicity, formed a stable complex with SENP2 via four to seven hydrogen bonds, and constituted more stable MD plots. Therefore, depending upon the outcomes presented herein, Betanin significantly inhibited SENP2 and hence may be considered as a suitable natural compound for the treatment of heart failure. Further clinical trials must be conducted to validate its use as a potential SENP2 inhibitor.
Keywords: SENP2; betanin; heart failure; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulation; natural compounds.
Copyright © 2022 Taghvaei, Sabouni and Minuchehr.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of novel anti-cancer agents, applying in silico method for SENP1 protease inhibition.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Sep;40(14):6228-6242. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1880480. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33533323
-
Enhanced desumoylation in murine hearts by overexpressed SENP2 leads to congenital heart defects and cardiac dysfunction.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Mar;52(3):638-49. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.11.011. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22155005 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-specific protease 2-mediated deSUMOylation is required for NDRG2 stabilization in gastric cancer cells.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Dec 12;21(1):195-201. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170651. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 29060933
-
SUMO1/sentrin/SMT3 specific peptidase 2 modulates target molecules and its corresponding functions.Biochimie. 2018 Sep;152:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 29908207 Review.
-
Betanin--a food colorant with biological activity.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015 Jan;59(1):36-47. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400484. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015. PMID: 25178819 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Notch signaling pathways with natural bioactive compounds: a promising approach against cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1412669. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1412669. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39092224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational study of SENP1 in cancer by novel natural compounds and ZINC database screening.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 12;14:1144632. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1144632. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37502217 Free PMC article.
-
SENP1-Mediated HSP90ab1 DeSUMOylation in Cardiomyocytes Prevents Myocardial Fibrosis by Paracrine Signaling.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(34):e2400741. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400741. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38992961 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products targeting inflammation-related metabolic disorders: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 2;9(6):e16919. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16919. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37346355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham M. J., Van Der Spoel D., Lindahl E., Hess B. (2014). “The GROMACS Development Team” in GROMACS User Manual Version 5.0. KTH (Sweden: Royal Institute of Technology, Solna, Sweden and Uppsala University; ).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

