Targeted CUL4A inhibition synergizes with cisplatin to yield long-term survival in models of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through a DDB2-mediated mechanism
- PMID: 35428778
- PMCID: PMC9012827
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04798-6
Targeted CUL4A inhibition synergizes with cisplatin to yield long-term survival in models of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through a DDB2-mediated mechanism
Abstract
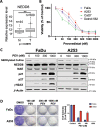
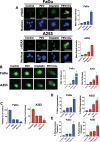
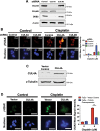
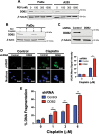
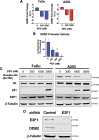
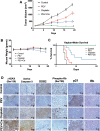
Patients with late-stage and human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) continue to have a very poor prognosis. The development of more effective novel therapies that improve overall survival and overcome drug resistance is an urgent priority. Here we report that HNSCC tumors significantly overexpress NEDD8 and exhibit high sensitivity to the first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor pevonedistat. Additional studies established that disruption of NEDD8-mediated protein turnover with pevonedistat dramatically augmented cisplatin-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in HNSCC models. Further analysis revealed that the specific pevonedistat target CUL4A played an essential role in driving the synergy of the pevonedistat and cisplatin combination. Targeted inhibition of CUL4A resulted in significant downregulation in Damage Specific DNA binding protein 2 (DDB2), a DNA-damage recognition protein that promotes nucleotide excision repair and resistance to cisplatin. Silencing of CUL4A or DDB2 enhanced cisplatin-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in a manner similar to that of pevonedistat demonstrating that targeted inhibition of CUL4A may be a novel approach to augment cisplatin therapy. Administration of pevonedistat to mice bearing HNSCC tumors significantly decreased DDB2 expression in tumor cells, increased DNA damage and potently enhanced the activity of cisplatin to yield tumor regression and long-term survival of all animals. Our findings provide strong rationale for clinical investigation of CUL4A inhibition with pevonedistat as a novel strategy to augment the efficacy of cisplatin therapy for patients with HNSCC and identify loss of DDB2 as a key pharmacodynamic mediator controlling sensitivity to this regimen.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATR inhibition sensitizes HPV- and HPV+ head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin.Oral Oncol. 2019 Aug;95:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.05.028. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Oral Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31345392 Free PMC article.
-
Wee-1 Kinase Inhibition Sensitizes High-Risk HPV+ HNSCC to Apoptosis Accompanied by Downregulation of MCl-1 and XIAP Antiapoptotic Proteins.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 1;21(21):4831-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0279. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26124202 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 and MRN synergy in platinum-based chemoresistance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2020 Mar;122(5):640-647. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0697-x. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31853007 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the RICTOR/mTORC2 complex enhances the response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to PI3K inhibition.Mol Oncol. 2019 Oct;13(10):2160-2177. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12558. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31393061 Free PMC article.
-
Combined EGFR1 and PARP1 Inhibition Enhances the Effect of Radiation in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Models.Radiat Res. 2020 Nov 10;194(5):519-531. doi: 10.1667/RR15480.1. Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32936912 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A protein with broad functions: damage-specific DNA-binding protein 2.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Dec;49(12):12181-12192. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07963-4. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36190612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Double-Edged Effects of MLN4924: Rethinking Anti-Cancer Drugs Targeting the Neddylation Pathway.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 21;14(7):738. doi: 10.3390/biom14070738. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting NEDDylation is a Novel Strategy to Attenuate Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Feb 13;3(2):245-257. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0340. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 36860653 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in colorectal cancer research: Unveiling the cellular and molecular mechanisms of neddylation (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Apr;64(4):39. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5627. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38391033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

