Effect of 6-Methoxybenzoxazolinone on the Cecal Microbiota of Adult Male Brandt's Vole
- PMID: 35422782
- PMCID: PMC9002351
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.847073
Effect of 6-Methoxybenzoxazolinone on the Cecal Microbiota of Adult Male Brandt's Vole
Abstract
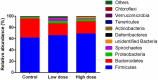
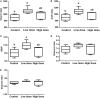
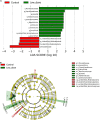
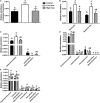
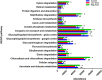
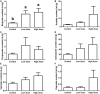
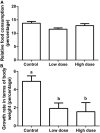
The anti-microbial effects of plant secondary metabolite (PSM) 6-methoxybenzoxazolinone (6-MBOA) have been overlooked. This study investigated the effect of 6-MBOA on the cecal microbiota of adult male Brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii), to evaluate its effect on the physiology of mammalian herbivores. The growth of voles was inhibited by 6-MBOA. A low dose of 6-MBOA enhanced the observed species, as well as the Chao1 and abundance-based coverage estimator (ACE) indices and introduced changes in the structure of cecal microbiota. The abundance of the phylum Tenericutes, classes Mollicutes and Negativicutes, order Selenomonadales, families Ruminococcaceae and Veillonellaceae, genera Quinella, Caproiciproducens, Anaerofilum, Harryflintia, and unidentified Spirochaetaceae in the cecal microbiota was enhanced upon administration of a low dose of 6-MBOA, which also inhibited glucose metabolism and protein digestion and absorption in the cecal microbiota. 6-MBOA treatment also stimulated butyrate production and dose-dependently enhanced the metabolism of xenobiotics in the cecal microbiome. Our findings indicate that 6-MBOA can affect Brandt's voles by inducing changes in the abundance of cecal bacteria, thereby, altering the contents of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and pathway intermediates, ultimately inhibiting the growth of voles. Our research suggests that 6-MBOA could potentially act as a digestion-inhibiting PSM in the interaction between mammalian herbivores and plants.
Keywords: 6-MBOA; Brandt’s vole; KEGG pathway analysis; SCFAs; cecal microbiota.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Chen, Liu, Liu, Jiang, Xu, Wang, Yang and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tannic Acid Induces Intestinal Dysfunction and Intestinal Microbial Dysregulation in Brandt's Voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii).Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;13(4):586. doi: 10.3390/ani13040586. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830373 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 6-methoxybenzoxazolinone (6-MBOA) on animals: state of knowledge and open questions.Naturwissenschaften. 2024 Aug 14;111(5):45. doi: 10.1007/s00114-024-01930-8. Naturwissenschaften. 2024. PMID: 39141101 Review.
-
Effect of photoperiod and 6-methoxybenzoxazolinone (6-MBOA) on the reproduction of male Brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii).Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2017 May 15;246:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28279674
-
Reproductive responses of male Brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii) to 6-methoxybenzoxazolinone (6-MBOA) under short photoperiod.Naturwissenschaften. 2016 Apr;103(3-4):29. doi: 10.1007/s00114-016-1347-2. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Naturwissenschaften. 2016. PMID: 26940061
-
Multiple infections of zoonotic pathogens in wild Brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii).Vet Med Sci. 2023 Sep;9(5):2201-2211. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1214. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37491010 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tannic Acid Induces Intestinal Dysfunction and Intestinal Microbial Dysregulation in Brandt's Voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii).Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;13(4):586. doi: 10.3390/ani13040586. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830373 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Food Restriction on Food Grinding in Brandt's Voles.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 5;13(21):3424. doi: 10.3390/ani13213424. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958179 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 6-methoxybenzoxazolinone (6-MBOA) on animals: state of knowledge and open questions.Naturwissenschaften. 2024 Aug 14;111(5):45. doi: 10.1007/s00114-024-01930-8. Naturwissenschaften. 2024. PMID: 39141101 Review.
-
Role of inflammatory cytokines and the gut microbiome in vascular dementia: insights from Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1398618. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1398618. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39247699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alibhai S. K. (1986). Reproductive response of Gerbillus harwoodii to 6-MBOA in Kora National Reserve, Kenya. J. Trop. Ecol. 2 377–379. 10.1017/S0266467400001012 - DOI
-
- Argandoña V. H., Niemeyer H. M., Corcuera L. J. (1981). Effect of content and distribution of hydroxamic acids on infestation in the aphid Schizaphis graminum. Phytochemistry 20 673–676. 10.1016/0031-9422(81)85154-0 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

