Non-toxic nature of chebulinic acid on biochemical, hematological and histopathological analysis in normal Sprague Dawley rats
- PMID: 35419271
- PMCID: PMC8960548
- DOI: 10.1007/s43188-021-00092-3
Non-toxic nature of chebulinic acid on biochemical, hematological and histopathological analysis in normal Sprague Dawley rats
Abstract
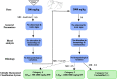
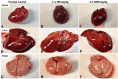
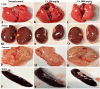
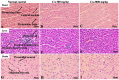
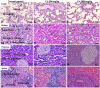
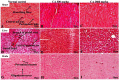
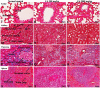
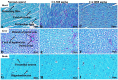
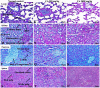
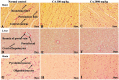
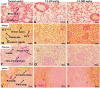
Chebulinic acid (CA) is an ellagitannins isolated from the dried fruits of Terminalia chebula with diverse pharmacological activities. The present study focused on the acute toxicity of CA in normal Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. CA was administered via oral gavage to different groups in 300 and 2000 mg/kg body weight and vehicle respectively. All the animals were monitored carefully for any physiological or behavioral changes for 14 days. On day 15th animals were euthanized and blood was collected for hematological and biochemical analysis. Different tissues were collected for histopathological study using four different staining techniques (hematoxylin and eosin, Masson's trichrome, periodic acid Schiff and picro sirius red) to observe any pathological alterations. The results highlighted no morbidity and mortality after oral ingestion of CA (300 and 2000 mg/kg). Food and water consumption, body weight, relative organ weight, hematological and biochemical parameters were normal without any gross pathological lesions in harvested tissues. The outcome of the current study supported safety of CA even at high dose. However, further detailed study is required on experimentally disease model to unfold its therapeutic potential in laboratory animals.
Keywords: Acute oral toxicity; Biochemical analysis; Chebulinic acid; Hematological; Histopathology.
© Crown 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Food additive "lauric acid" possess non-toxic profile on biochemical, haematological and histopathological studies in female Sprague Dawley (SD) rats.PeerJ. 2020 Mar 31;8:e8805. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8805. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32266118 Free PMC article.
-
Oral toxicity of arjunolic acid on hematological, biochemical and histopathological investigations in female Sprague Dawley rats.PeerJ. 2019 Nov 22;7:e8045. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8045. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31772835 Free PMC article.
-
NTP Research Report on the CLARITY-BPA Core Study: A Perinatal and Chronic Extended-Dose-Range Study of Bisphenol A in Rats: Research Report 9 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2018 Sep. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2018 Sep. PMID: 31305969 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Evaluation of safety of iridoids rich fraction from Valeriana jatamansi Jones: Acute and sub-chronic toxicity study in mice and rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Aug 22;172:386-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.046. Epub 2015 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26164073
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of 4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol (CASRN 34885-03-5) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats (Gavage Studies): DART Report 02 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2020 Jun. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2020 Jun. PMID: 32749828 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Subacute Toxicity Effects of the Aqueous Shoot Extract of Yushania alpina (K. Schum.) W.C.Lin in Sprague Dawley Rats: An Appraisal of Its Safety in Ethnomedicinal Usage.J Toxicol. 2022 Aug 25;2022:6283066. doi: 10.1155/2022/6283066. eCollection 2022. J Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36061215 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

