Identification of a pyroptosis-related lncRNA risk model for predicting prognosis and immune response in colon adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35413978
- PMCID: PMC9004096
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02572-8
Identification of a pyroptosis-related lncRNA risk model for predicting prognosis and immune response in colon adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) is one of the most common malignant tumors and is diagnosed at an advanced stage with a poor prognosis worldwide. Pyroptosis is involved in the initiation and progression of tumors. This research focused on constructing a pyroptosis-related ceRNA network to generate a reliable risk model for risk prediction and immune infiltration analysis of COAD.
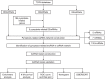
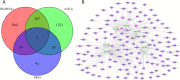
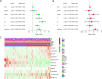
Methods: Transcriptome data, miRNA-sequencing data, and clinical information were downloaded from the TCGA database. First, differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs), miRNAs (DEmiRNAs), and lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) were identified to construct a pyroptosis-related ceRNA network. Second, a pyroptosis-related lncRNA risk model was developed applying univariate Cox regression analysis and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator method (LASSO) regression analysis. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analyses were utilized to functionally annotate RNAs contained in the ceRNA network. In addition, Kaplan-Meier analysis, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, univariate and multivariate Cox regression, and nomogram were applied to validate this risk model. Finally, the relationship of this risk model with immune cells and immune checkpoint blockade (ICB)-related genes was analyzed.
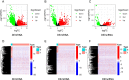
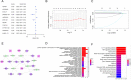
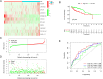
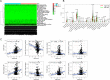
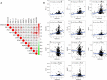
Results: A total of 5373 DEmRNAs, 1159 DElncRNAs, and 355 DEmiRNAs were identified. A pyroptosis-related ceRNA regulatory network containing 132 lncRNAs, 7 miRNAs, and 5 mRNAs was constructed, and a ceRNA-based pyroptosis-related risk model including 11 lncRNAs was built. The tumor tissues were classified into high- and low-risk groups according to the median risk score. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the high-risk group had a shorter survival time; ROC analysis, independent prognostic analysis, and nomogram further indicated the risk model was a significant independent prognostic factor what had an excellent ability to predict patients' risk. Moreover, immune infiltration analysis indicated that the risk model was related to immune infiltration cells (i.e., B cell naïve, T cell follicular helper, macrophage M1) and ICB-related genes (i.e., PD-1, CTLA4, HAVCR2).
Conclusions: This pyroptosis-related lncRNA risk model possessed good prognostic value, and the ability to predict the outcome of ICB immunotherapy in COAD.
Keywords: Colon adenocarcinoma; Immunotherapy; Pyroptosis; Tumor immune microenvironment; ceRNA network.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening Prognosis-Related lncRNAs Based on WGCNA to Establish a New Risk Score for Predicting Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Immunol Res. 2021 Aug 14;2021:5518908. doi: 10.1155/2021/5518908. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34426790 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 27;16(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1640-2. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30261893 Free PMC article.
-
The noncoding RNAs regulating pyroptosis in colon adenocarcinoma were derived from the construction of a ceRNA network and used to develop a prognostic model.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Sep 20;15(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01359-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36127676 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
Identification of MFI2-AS1, a Novel Pivotal lncRNA for Prognosis of Stage III/IV Colorectal Cancer.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Dec;65(12):3538-3550. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06064-1. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31960204 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis of the Regulation and Prognostic Effect of Coat Complex Subunit Zeta 1.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 10;14(4):889. doi: 10.3390/genes14040889. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107648 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Validation of Pyroptosis-Related lncRNA Prediction Model for Colon Adenocarcinoma and Immune Infiltration Analysis.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 17;2022:4492608. doi: 10.1155/2022/4492608. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36168326 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the effect of pyroptosis on the occurrence, development, invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):3410-3427. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i8.3410. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39171180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel prognostic model predicts overall survival in colon cancer based on RNA splicing regulation gene expression.Cancer Sci. 2022 Oct;113(10):3330-3346. doi: 10.1111/cas.15480. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35792657 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs are involved in tumor cell death and affect tumorigenesis, progression, and treatment: a systematic review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 28;12:1284934. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1284934. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38481525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

