RPL15 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of RPs-MDM2-p53 signaling pathway
- PMID: 35410346
- PMCID: PMC9003963
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02555-5
RPL15 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of RPs-MDM2-p53 signaling pathway
Abstract
Backround: RPL15 has been found to participate in human tumorigenesis. However, its function and regulatory mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development are still unclear. Current study investigated the effects of RPL15 in HCC.
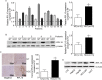
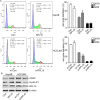
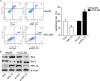
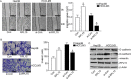
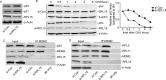
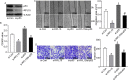
Methods: The expression of RPL15 in clinical tissues and cell lines of HCC was detected by RT-qPCR, Western blotting, and Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Colony formation, CCK-8, flow cytometry, Wound healing and Transwell invasion assays, were used to detect the carcinoma progression of HCC cells with RPL15 overexpression or knockdown in vitro. A xenograft model was constructed to assess the effect of RPL15 knockdown on HCC cells in vivo. The expression of CDK2 and Cyclin E1 related to cell cycles, Bax and Bcl-2 related to cell apoptosis, E-cadherin, N-cadherin and Vimentin related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), p53 and p21 related to p53 signaling pathway, were detected by Western blotting. The connection between p53, MDM2 and RPL5/11 affected by RPL15 was analyzed using immunoprecipitation and Cycloheximide (CHX) chase assay.
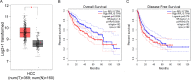
Results: Elevated RPL15 was identified in HCC tissues, which was not only a prediction for the poor prognosis of HCC patients, but also associated with the malignant progression of HCC. RPL15 silencing arrested HCC cell cycle, suppressed HCC cell colony formation, proliferation, invasion, and migration, and induce cell apoptosis. On the contrary, RPL15 upregulation exerted opposite effects. Results also indicated that HCC cell invasion and migration were associated with EMT, and that the RPs-MDM2-p53 pathway was implicated in RPL15-mediated oncogenic transformation. In addition, RPL15 knockdown significantly suppressed HCC xenografts growth.
Conclusions: RPL15 played crucial roles in HCC progression and metastasis, serving as a promising candidate for targeted therapies.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; MDM2; RPL15; Tumor progression; p53.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
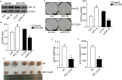
Similar articles
-
EXOSC10 is a novel hepatocellular carcinoma prognostic biomarker: a comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experiment verification.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 8;11:e15860. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15860. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37701829 Free PMC article.
-
PHF8 upregulation contributes to autophagic degradation of E-cadherin, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 4;37(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0890-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30180906 Free PMC article.
-
TPX2 Level Correlates with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and EMT.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Aug;60(8):2360-72. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3730-9. Epub 2015 May 30. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26025609
-
The role of MDM2-p53 axis dysfunction in the hepatocellular carcinoma transformation.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Jun 19;6:53. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0287-y. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 32595984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of p53 suppression in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2023 Jun 1;14(3):46-70. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v14.i3.46. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37304923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of Camptothecin Anticancer Drugs with Ribosomal Proteins L15 and L11: A Molecular Docking Study.Molecules. 2023 Feb 15;28(4):1828. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041828. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838813 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Anticancer Mechanism of OR3 Pigment from Streptomyces coelicolor JUACT03 Against the Human Hepatoma Cell Line Using a Proteomic Approach.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):1061-1077. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01258-0. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38578403
-
Ribosomal proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma: mysterious but promising.Cell Biosci. 2024 Nov 1;14(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01316-3. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39487553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in primary open-angle glaucoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Nov 15;16(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01722-5. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37968618 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Deregulated Ribosomal Biogenesis in Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 30;13(11):1593. doi: 10.3390/biom13111593. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002277 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Shi JJ, Dang SS. Recent advances in molecular targeted therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. World Chin J Dig. 2018;26(34):2008–2017. doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v26.i34.2008. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

