Silencing LINC00491 Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Progression through MiR-188-5p-induced Inhibition of ZFP91
- PMID: 35399733
- PMCID: PMC8990418
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.65071
Silencing LINC00491 Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Progression through MiR-188-5p-induced Inhibition of ZFP91
Abstract
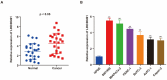
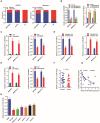
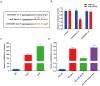
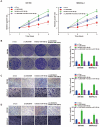
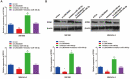
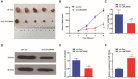
Background: Pancreatic cancer is recognized as one of the most malignant tumors with poor prognosis. Recently, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are considered as a potential prognostic biomarker of PC. However, the concrete biological effect of lncRNAs in PC remains unmasked. Herein, we explored the mechanism of LINC00491 in PC. Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was administrated to detected the expression of LINC00491 in PC tissues and cell lines. Loss-of-function experiment in vitro and in vivo was carried out to figure out the biological effects of LINC00491 on PC carcinogenesis. Luciferase reporter assay, subcellular fractionation, western blotting, pull-down assay and RNA immunoprecipitation assay were further used to explore the mechanism of PC tumorigenesis of LINC00491. Results: An increase of LINC00491 was detected in PC cell lines and tissues. Silencing LINC00491 in vitro and in vivo subsequently hindered cell migration, invasion, proliferation and tumor growth, respectively. Further research confirmed a negative and a positive connection of LINC00491 with microRNA 188-5p (miR-188-5p) level and Zinc finger protein 91 (ZFP91), a target of miR-188-5p, respectively. qRT-PCR and western blotting found that miR-188-5p was upregulated while LINC00491 was downregulated, concomitant with ZFP91 decreasing in PC cells or node mouse tumors, which could be significantly restored by inhibiting miR-188-5p. Besides, overexpression of miR-188-5p partially restored the inhibitory effect of LINC00491 diminution on proliferation, migration, and invasion of PC cells. Conclusion: LINC00491 promotes PC proliferation, migration, invasion via the miR-188-5p/ZFP91 axis, suggesting LINC00491 could be a new therapeutic target for PC.
Keywords: LINC00491; ZFP91; carcinogenesis; miR-188-5p; pancreatic cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LINC00491 Contributes to the Malignancy of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer via Competitively Binding to microRNA-324-5p and Thereby Increasing Specificity Protein 1 Expression.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 6;12:6779-6793. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S264681. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. Retraction in: Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Sep 29;13:7505-7506. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S341520 PMID: 32821159 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
LINC01128 facilitates the progression of pancreatic cancer through up-regulation of LDHA by targeting miR-561-5p.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Feb 22;22(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02490-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35193567 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC00514 accelerates pancreatic cancer progression by acting as a ceRNA of miR-28-5p to upregulate Rap1b expression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 8;39(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01660-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32771045 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00491 promotes cell growth and metastasis through miR-324-5p/ROCK1 in liver cancer.J Transl Med. 2021 Dec 7;19(1):504. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03139-z. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34876144 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing LINC00491 inhibits prostate cancer development through the miR-384/TRIM44 axis.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Jul;37(7):e23370. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23370. Epub 2023 Apr 17. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37070216
Cited by
-
BioKA: a curated and integrated biomarker knowledgebase for animals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D1121-D1130. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad873. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 37843156 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of virus-encoded circular RNAs in host cells.Microb Genom. 2022 Jun;8(6):mgen000848. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000848. Microb Genom. 2022. PMID: 35731570 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

