Pan-cancer Bioinformatics Analysis of the Double-edged Role of Hypoxia-inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) in Human Cancer
- PMID: 35399173
- PMCID: PMC8962818
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10104
Pan-cancer Bioinformatics Analysis of the Double-edged Role of Hypoxia-inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) in Human Cancer
Abstract
Background/aim: Despite the emergence of cellular, animal, and clinical-based evidence demonstrating a link between hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and malignancy, the comprehensive assessment of HIF-1α in pan-cancer patients remains unclear, particularly regarding HIF-1α expression and its association with immune infiltration and immune checkpoint. The present study aimed to investigate the role of HIF-1α expression in various types of malignancies through bioinformatics analysis.
Materials and methods: We investigated the expression and prognostic value of HIF-1α in pan-cancer based on the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) dataset. The abundance of immune infiltration was estimated by xCell immune deconvolution methods. We investigated the relationship of HIF-1α expression with immune infiltration and immune checkpoint gene expression, with a focus on gastric adenocarcinoma (STAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC).
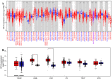
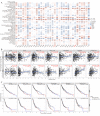
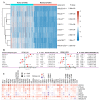
Results: HIF-1α expression had different effects on the prognosis of various cancers. In contrast to the protective effect of HIF-1α expression in LUSC, high levels of HIF-1α expression played a detrimental role in the survival of STAD patients. There was a significant positive correlation between HIF-1α expression and immune infiltration in STAD patients, including regulatory T-cells (Tregs), T-cell CD4+ Th2, neutrophils, M1 and M2 macrophages. In addition, immune checkpoint molecules showed different HIF-1α-related profiles in various carcinomas.
Conclusion: A relatively comprehensive view of the oncogenic role of HIF-1α in various tumors based on a pan-cancer analysis is provided in this study. HIF-1α may be considered a poor prognostic biomarker for STAD and, moreover, it may be involved in regulating tumor immune infiltration.
Keywords: HIF-1α; Hypoxia; cancer prognosis; immune checkpoint; immune infiltration.
Copyright 2022, International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
WNT5A in Cancer: A Pan-Cancer Analysis Revealing Its Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Potential.Cureus. 2024 Jul 23;16(7):e65190. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65190. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39176352 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis of PARP1 Alterations as Biomarkers in the Prediction of Immunotherapeutic Effects and the Association of Its Expression Levels and Immunotherapy Signatures.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 31;12:721030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.721030. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34531868 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and immunological role of Fam20C in pan-cancer.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jan 29;41(1):BSR20201920. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201920. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33306121 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Jun;36(3):321-327. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1586-7. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27376798 Review.
-
The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and its clinical significance in lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Swiss Med Wkly. 2013 Sep 6;143:w13855. doi: 10.4414/smw.2013.13855. eCollection 2013. Swiss Med Wkly. 2013. PMID: 24018850 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
