Cardiovascular magnetic resonance characterization of rheumatic mitral stenosis: findings from three worldwide endemic zones
- PMID: 35387660
- PMCID: PMC8988335
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-022-00853-5
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance characterization of rheumatic mitral stenosis: findings from three worldwide endemic zones
Abstract
Background: Cardiac remodeling in rheumatic mitral stenosis (MS) is complex and incompletely understood. The objective of this study was to evaluate cardiac structural and functional changes in a cohort of patients with rheumatic MS using cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR).
Methods: This retrospective study included 40 patients with rheumatic MS, consisting of 19 patients from India, 15 patients from China, and 6 patients from Mexico (median (interquartile range (IQR)) age: 45 years (34-55); 75% women). Twenty patients were included in the control group. CMR variables pertaining to morphology and function were collected. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) sequences were acquired for tissue characterization. Statistical analyses were performed using the Kruskal-Wallis test and the chi-square test.
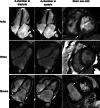
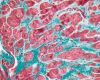
Results: Compared to the control group, patients with MS had lower left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (51% (42%-55%) vs 60% (57%-65%), p < 0.001), lower right ventricular (RV) ejection fraction (44% (40%-52%) vs 64% (59%-67%), p < 0.001), higher RV end-diastolic volume (72 (58-87) mL/m2 vs 59 (49-69) mL/m2, p = 0.003), larger left atrial volume (87 (67-108) mL/m2 vs 29 (22-34) mL/m2, p < 0.001), and right atrial areas (20 (16-23) cm2 vs 13 (12-16) cm2, p < 0.001). LGE was prevalent in patients with rheumatic MS (82%), and was commonly located at the RV insertion sites. Furthermore, the patient cohorts from India, China, and Mexico were heterogeneous in terms of baseline characteristics and cardiac remodeling.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that biventricular dysfunction, right and left atrial remodeling, and LGE at the RV insertion sites are underappreciated in contemporary rheumatic MS. Further studies are needed to elucidate the prognostic implications of these findings.
Keywords: Cardiac remodeling; Cardiovascular magnetic resonance; Rheumatic mitral stenosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between late gadolinium enhancement and global longitudinal strain in patients with rheumatic mitral stenosis.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 May;35(5):781-789. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-1511-1. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30556113
-
Prognostic Value of Right Ventricular Function in Patients With Suspected Myocarditis Undergoing Cardiac Magnetic Resonance.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Jan;16(1):28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2022.08.011. Epub 2022 Oct 19. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36599567
-
Cardiac Involvement in Patients Recovered From COVID-2019 Identified Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Nov;13(11):2330-2339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 May 12. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32763118 Free PMC article.
-
Right and left ventricular interactions, strain, and remodeling in repaired pulmonary stenosis patients with preserved right ventricular ejection fraction: A cardiac magnetic resonance study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Jul;52(1):129-138. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27034. Epub 2020 Jan 24. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31975534
-
Cardiac reverse remodeling in primary mitral regurgitation: mitral valve replacement vs. mitral valve repair.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2023 Jul 27;25(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12968-023-00946-9. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2023. PMID: 37496072 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cardiac imaging in rheumatic heart disease and future developments.Eur Heart J Open. 2023 Feb 20;3(2):oeac060. doi: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeac060. eCollection 2023 Mar. Eur Heart J Open. 2023. PMID: 36876318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left atrial strain by cardiac MRI feature tracking in mitral stenosis before and after balloon valvuloplasty.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Sep;40(9):1971-1978. doi: 10.1007/s10554-024-03190-z. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39115614
References
-
- Marijon E, Mocumbi A, Narayanan K, Jouven X, Celermajer DS. Persisting burden and challenges of rheumatic heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2021;1:ehab407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

