Regulatory effects of a novel cysteine protease inhibitor in Baylisascaris schroederi migratory larvae on mice immune cells
- PMID: 35379304
- PMCID: PMC8981815
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-022-05240-8
Regulatory effects of a novel cysteine protease inhibitor in Baylisascaris schroederi migratory larvae on mice immune cells
Abstract
Background: The giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) is a well-known, rare and endangered species. Baylisascaris schroederi is a pathogenic ascarid. Infection with B. schroederi may cause death in giant pandas. At present, the immune evasion mechanism of B. schroederi is little known. Cysteine protease inhibitors (CPI) play important roles in the regulation of host immune responses against certain nematodes. In this study, we focused on the analysis of the regulation of B. schroederi migratory larvae CPI (rBsCPI-1) on mice immune cells.
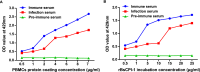
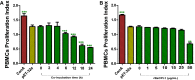
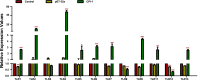
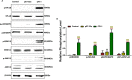
Methods: First, the pattern recognition receptors on the surface of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and the signal pathways that transduce extracellular signals into the nucleus activated by rBsCPI-1 were identified. Then, the regulatory effects of rBsCPI-1 on PBMCs physiological activities were detected. Finally, the effects of rBsCPI-1 on TLR signaling pathway activation and NF-κB phosphorylation in mice immunized with recombinant protein were analysed.
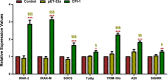
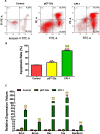
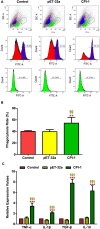
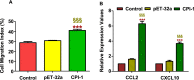
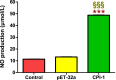
Results: The results suggested that rBsCPI-1 secreted by B. schroederi migratory larvae is mainly recognized by TLR2 and TLR4 on PBMCs. Extracellular signals are transduced into the nucleus through the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, enhancing the phagocytosis, migration, and apoptosis of PBMCs; meanwhile, rBsCPI-1 induces high expression of NO. Thus, rBsCPI-1 plays a role in immune regulation. In addition, the high expression of negative regulatory factors also ensured that TLR activation is maintained at the optimal level.
Conclusions: rBsCPI-1 can transduce regulatory signals into immune cells by activating the TLR2/4-NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway, having a certain regulatory effect on the physiological activities. Meanwhile, rBsCPI-1 can maintain the immune response in a balance by limiting the over-activation of the TLRs signaling pathway and thus contributes to B. schroederi immune evasion.
Keywords: Baylisascaris schroederi; Cysteine protease inhibitor; Immune evasion mechanism; PBMC; TLRs signal pathway.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel cysteine protease inhibitor in Baylisascaris schroederi migratory larvae regulates inflammasome activation through the TLR4-ROS-NLRP3 pathway.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Sep 23;15(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05466-6. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36151570 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel cysteine protease inhibitor in Baylisascaris schroederi migratory larvae and its role in regulating mice immune cell response.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 29;13:894820. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.894820. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36105820 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular diagnosis of Baylisascaris schroederi infections in giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) feces using PCR.J Wildl Dis. 2013 Oct;49(4):1052-5. doi: 10.7589/2012-07-175. J Wildl Dis. 2013. PMID: 24502740
-
Baylisascariosis--infections of animals and humans with 'unusual' roundworms.Vet Parasitol. 2013 Apr 15;193(4):404-12. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.036. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Vet Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23339846 Review.
-
Review on parasites of wild and captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca): Diversity, disease and conservation impact.Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2020 Jul 28;13:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2020.07.007. eCollection 2020 Dec. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2020. PMID: 32793415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel cysteine protease inhibitor in Baylisascaris schroederi migratory larvae regulates inflammasome activation through the TLR4-ROS-NLRP3 pathway.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Sep 23;15(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05466-6. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36151570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei F, Swaisgood R, Hu Y, Nie Y, Yan L, Zhang Z, et al. Progress in the ecology and conservation of giant pandas. Conserv Biol. 2015;29:1497–1507. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JS, Daszak P, Huang HL, Yang GY, Kilpatrick AM, Zhang SY. Parasite threat to panda conservation. EcoHealth. 2008;5:6–9. - PubMed
-
- Peng Z, Zhang C, Shen M, Bao H, Hou Z, He S, et al. Baylisascaris schroederi Infection in Giant Pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) in Foping National Nature Reserve. China J Wildl Dis. 2017;53:854–858. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Zhang Z, Wang C, Lan J, Li Y, Chen Z, et al. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Baylisascaris schroederi, Baylisascaris ailuri and Baylisascaris transfuga from giant panda, red panda and polar bear. Gene. 2011;482:59–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

