NTRK Fusion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Therapy, and TRK Inhibitor Resistance
- PMID: 35372074
- PMCID: PMC8968138
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.864666
NTRK Fusion in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Therapy, and TRK Inhibitor Resistance
Abstract
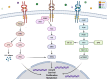
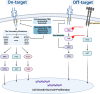
Neurotrophic tropomyosin receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion has been identified as an oncogenic driver of various solid tumors, and it is rare in non-smalll cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a frequency of approximately less than 1%. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is of priority for detecting NTRK fusions, especially RNA-based NGS. Currently, the tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK) inhibitors have shown promising efficacy and well tolerance in patients with NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors, regardless of tumor histology. The first-generation TRK inhibitors (larotrectinib and entrectinib) are recommended as the first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC patients with positive NTRK fusion. However, TRK inhibitor resistance can eventually occur due to on-target or off-target mechanisms. Further studies are under investigation to overcome resistance and improve survival. Interestingly, NTRK fusion might be the mechanism of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation. Regarding immunotherapy, the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in NSCLC patients harboring NTRK fusion has yet to be well described. In this review, we elucidate the function of NTRK genes, summarize the diagnostic techniques for NTRK fusions, and present clinical data for TRK inhibitors; we also discuss potential mechanisms of resistance to TRK inhibitors.
Keywords: NTRK fusion; TRK inhibitor; diagnosis; non-small cell lung cancer; resistance.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Wei, Zhang, Jiang, Zhang and Chu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NTRK Fusion-positive Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: The Diagnosis and Targeted Therapy.Clin Lung Cancer. 2021 Jan;22(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.10.013. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33272813 Review.
-
How selecting best therapy for metastatic NTRK fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer?Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Dec;9(6):2535-2544. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-434. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33489816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing of NTRK Gene Fusion Testing and Treatment Modifications Following TRK Fusion Status Among US Oncologists Treating TRK Fusion Cancer.Target Oncol. 2022 May;17(3):321-328. doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00887-w. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Target Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35716252 Free PMC article.
-
NTRK fusions in lung cancer: From biology to therapy.Lung Cancer. 2021 Nov;161:108-113. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.09.005. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34563714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NTRK gene fusion testing and management in lung cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2024 Jun;127:102733. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102733. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Cancer Treat Rev. 2024. PMID: 38733648 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenocarcinomas of the Lung and Neurotrophin System: A Review.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 10;10(10):2531. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102531. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust Performance of the Novel Research-Use-Only Idylla GeneFusion Assay Using a Diverse Set of Pathological Samples with a Proposed 1-Day Workflow for Advanced NSCLC Evaluation.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 31;15(1):292. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010292. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612287 Free PMC article.
-
NTRK Gene Fusions in Solid Tumors and TRK Inhibitors: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series.J Pers Med. 2022 Nov 2;12(11):1819. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111819. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36579526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Molecular Determinants of Therapeutic Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6961. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136961. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting immune cell types of tumor microenvironment to overcome resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in lung cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1132158. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1132158. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36874015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous