Stem Cell Therapy for Thyroid Diseases: Progress and Challenges
- PMID: 35371349
- PMCID: PMC8968462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2022.100665
Stem Cell Therapy for Thyroid Diseases: Progress and Challenges
Abstract
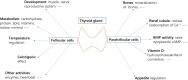
Background: Thyroid hormones are indispensable for organ development and maintaining homeostasis. Thyroid diseases, including thyroiditis and thyroid cancer, affect the normal secretion of hormones and result in thyroid dysfunction.
Objective: This review focuses on therapeutic applications of stem cells for thyroid diseases.
Methods: A literature search of Medline and PubMed was conducted (January 2000-July 2021) to identify recent reports on stem cell therapy for thyroid diseases.
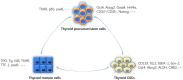
Results: Stem cells are partially developed cell types. They have the capacity to form specialized cells. Besides embryonic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, organ resident stem cells and cancer stem cells are recently reported to have important roles in forming organ specific cells and cancers. Stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells, have anti-inflammatory and anticancer functions as well.
Conclusions: This review outlines the therapeutic potency of embryonic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, thyroid resident stem cells, and thyroid cancer stem cells in thyroid cells' regeneration, thyroid function modulation, thyroiditis suppression, and antithyroid cancers. Stem cells represent a promising form of treatment for thyroid disorders.
Keywords: Autoimmune thyroid disorder; Stem cells; Thyroid diseases; Thyroid dysfunction.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical review: The emerging cell biology of thyroid stem cells.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Sep;96(9):2692-702. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1047. Epub 2011 Jul 21. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21778219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous, very small embryonic-like stem cells: critical review, therapeutic potential and a look ahead.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Dec;23(1):41-76. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw030. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27614362 Review.
-
Foetal and neonatal thyroid disorders.Minerva Pediatr. 2002 Oct;54(5):383-400. Minerva Pediatr. 2002. PMID: 12244277 Review. English, Italian.
-
[Effect of anti-thyroid antibodies on thyroid hormone secretion].Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1981 Sep;92(9):295-6. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1981. PMID: 7028173 Russian.
-
Stem cell biology in thyroid cancer: Insights for novel therapies.World J Stem Cells. 2014 Nov 26;6(5):614-9. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.614. World J Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 25426258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MYOFIBROBLASTS HINDER RECOVERY OF HASHIMOTO THYROIDITIS IN THE ULTRASTRUCTURAL LEVEL.Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2023 Oct-Dec;19(4):415-420. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2023.415. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2023. PMID: 38933253 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering a functional thyroid as a potential therapeutic substitute for hypothyroidism treatment: A systematic review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 2;13:1065410. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1065410. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36531472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delitala AP, Capobianco G, Cherchi PL, Dessole S, Delitala G. Thyroid function and thyroid disorders during pregnancy: a review and care pathway. Archives of gynecology and obstetrics. 2019;299:327–338. - PubMed
-
- Cabanillas ME, McFadden DG, Durante C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2783–2795. - PubMed
-
- Nagayama Y. Thyroid Autoimmunity and Thyroid Cancer - The Pathogenic Connection: A 2018 Update. 2018;50:922-31. - PubMed
-
- Glicksman MA. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: The Most Versatile Source for Stem Cell Therapy. Clinical therapeutics. 2018;40:1060–1065. - PubMed
-
- Dunn A, Talovic M, Patel K, Patel A, Marcinczyk M, Garg K. Biomaterial and stem cell-based strategies for skeletal muscle regeneration. Journal of orthopaedic research: official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2019;37:1246–1262. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

