[ANA- 12 inhibits spinal inflammation and alleviates acute and chronic pain in rats by targeted blocking of BDNF/TrkB signaling]
- PMID: 35365447
- PMCID: PMC8983361
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.02.09
[ANA- 12 inhibits spinal inflammation and alleviates acute and chronic pain in rats by targeted blocking of BDNF/TrkB signaling]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the inhibitory effect of ANA-12 that blocks brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)/ tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) signaling on inflammatory pain in rats and explore the underlying mechanism.
Methods: Forty-two adult SD rats were randomized into BDNF-induced acute pain group (n=24) and CFA-induced chronic pain group. The former group were randomly divided into 4 subgroups, including a control group, ANA-12 treatment group, BDNF treatment group, and BDNF+ANA-12 treatment group; the latter group were subgrouped into control group, CFA treatment group (CFA) and CFA + ANA-12 treatment group. The effects of ANA-12 treatment on pain behaviors of the rats with BDNF-induced acute pain and CFA-induced chronic inflammatory pain were observed. Western blotting was used to examine TrkB signaling and expressions of microglia marker protein Iba1 and TNF-α in the spinal cord of the rats.
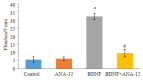
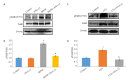
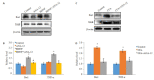
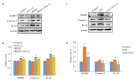
Results: BDNF injection into the subarachnoid space significantly increased the number of spontaneous paw withdrawal of the rats (P < 0.05), which was obviously reduced by ANA-12 treatment (P < 0.05). The rats with intraplantar injection of CFA, showed significantly increased ipsilateral mechanical stimulation sensitivity (P < 0.05), and ANA-12 treatment obviously increased the ipsilateral foot withdrawal threshold (P < 0.05). Treatment with either BDNF or CFA significantly increased the phosphorylation level of TrkB (Y705) in the spinal cord of the rats (P < 0.05), which was significantly lowered by ANA-12 treatment (P < 0.05). Treatment with BDNF and CFA both significantly up-regulated the expressions of Iba1 and TNF-α in the spinal cord (P < 0.05), but ANA-12 significantly reduced their expression levels (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: ANA-12 can reduce spinal cord inflammation and relieve acute and chronic pain in rats by targeted blocking of BDNF/TrkB signaling.
目的: 探讨ANA-12靶向阻断脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)/原肌球蛋白受体激酶B(TrkB)信号对炎症痛的抑制作用及机制。
方法: 将42只大鼠随机分为7组(6只/组):BDNF处理下的对照组、ANA-12处理组、BDNF处理组以及BDNF和ANA-12联合处理组(BDNF+ANA-12);炎症痛模型下的对照组、CFA处理组以及CFA和ANA-12联合处理组(CFA+ANA-12)。给药完毕后,对各组大鼠进行痛觉行为学检测,记录ANA-12处理对BDNF-急性痛和CFA-慢性炎症痛大鼠痛觉行为的影响;采用免疫印迹法检测各组大鼠脊髓组织TrkB信号、小胶质细胞标记蛋白Iba1和促炎细胞因子TNF-α以及炎症因子IL-1β、Caspase-1、NLRP3的表达水平。
结果: 与对照组相比,BDNF增加自发缩足次数(P < 0.05);与BDNF组相比,ANA-12降低自发缩足次数(P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,CFA增加同侧机械刺激敏感性(P < 0.05);与CFA组相比,ANA-12增加同侧缩足阈值(P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,BDNF和CFA增加磷酸化TrkB(Y705)水平(P < 0.05);与BDNF或CFA组相比,ANA-12降低TrkB(Y705)磷酸化水平(P < 0.05)。与对照组相比,BDNF和CFA上调Iba1、TNF-α以及炎症因子表达(P < 0.05);与BDNF或CFA组相比,ANA-12降低Iba1、TNF-α以及炎症因子表达水平(P < 0.05)。
结论: ANA-12靶向阻断BDNF/TrkB信号可降低脊髓炎症并缓解急性痛和慢性痛。
Keywords: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; microglia; pathological pain; tropomyosin receptor kinase B; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures
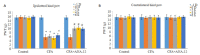
Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of dorsal root ganglia BDNF and trkB receptor in inflammatory pain: an in vivo and in vitro study.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Sep 30;8:126. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-126. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21958434 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF promotes activation of astrocytes and microglia contributing to neuroinflammation and mechanical allodynia in cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 13;17(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-1704-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31931832 Free PMC article.
-
The BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway is involved in heat hyperalgesia mediated by Cdk5 in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e85536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085536. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465591 Free PMC article.
-
[Analgesic effect and mechanism of electroacupuncture on SNI rats based on microglia-BDNF-neuron signal].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022 Sep 12;42(9):1029-36. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20210617-0004. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36075600 Chinese.
-
Opioid tolerance and opioid-induced hyperalgesia: Is TrkB modulation a potential pharmacological solution?Neuropharmacology. 2022 Dec 1;220:109260. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109260. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 36165856 Review.
Cited by
-
EA participates in pain transition through regulating KCC2 expression by BDNF-TrkB in the spinal cord dorsal horn of male rats.Neurobiol Pain. 2023 Jan 5;13:100115. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100115. eCollection 2023 Jan-Jul. Neurobiol Pain. 2023. PMID: 36875547 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
