Selective Retinoic Acid Receptor γ Antagonist 7C is a Potent Enhancer of BMP-Induced Ectopic Endochondral Bone Formation
- PMID: 35359440
- PMCID: PMC8963923
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.802699
Selective Retinoic Acid Receptor γ Antagonist 7C is a Potent Enhancer of BMP-Induced Ectopic Endochondral Bone Formation
Abstract
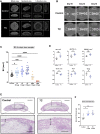
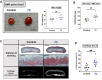
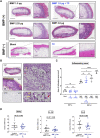
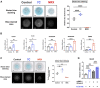
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) have been clinically applied for induction of bone formation in musculoskeletal disorders such as critical-sized bone defects, nonunions, and spinal fusion surgeries. However, the use of supraphysiological doses of BMP caused adverse events, which were sometimes life-threatening. Therefore, safer treatment strategies for bone regeneration have been sought for decades. Systemic administration of a potent selective antagonist of retinoic acid nuclear receptor gamma (RARγ) (7C) stimulated BMP-induced ectopic bone formation. In this study, we developed 7C-loaded poly lactic nanoparticles (7C-NPs) and examined whether local application of 7C enhances BMP-induced bone regeneration. The collagen sponge discs that absorbed recombinant human (rh) BMP-2 were implanted into the dorsal fascia of young adult mice to induce ectopic bone. The combination of rhBMP-2 and 7C-NP markedly increased the total bone volume and thickness of the bone shell of the ectopic bone in a dose-dependent manner compared to those with rhBMP-2 only. 7C stimulated sulfated proteoglycan production, expression of chondrogenic marker genes, and Sox9 reporter activity in both chondrogenic cells and MSCs. The findings suggest that selective RARγ antagonist 7C or the related compounds potentiate the bone inductive ability of rhBMP-2, as well as support any future research to improve the BMP-2 based bone regeneration procedures in a safe and efficient manner.
Keywords: Bmp/Smad signaling; RARγ inverse agonist; bone morphogenetic protein; bone regeneration; endochondral bone formation; retinoic acid receptor γ.
Copyright © 2022 Tateiwa, Kaito, Hashimoto, Okada, Kodama, Kushioka, Bal, Tsukazaki, Nakagawa, Ukon, Hirai, Tian, Alferiev, Chorny, Otsuru, Okada and Iwamoto.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of retinoic acid receptor γ function promotes endochondral bone formation.J Orthop Res. 2017 May;35(5):1096-1105. doi: 10.1002/jor.23347. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Orthop Res. 2017. PMID: 27325507 Free PMC article.
-
BMP-2/7 heterodimer strongly induces bone regeneration in the absence of increased soft tissue inflammation.Spine J. 2018 Jan;18(1):139-146. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.07.171. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 28735764
-
Sandwich-type PLLA-nanosheets loaded with BMP-2 induce bone regeneration in critical-sized mouse calvarial defects.Acta Biomater. 2017 Sep 1;59:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.06.041. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28666885
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
The importance of drug delivery to optimize the effects of bone morphogenetic proteins during periodontal regeneration.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2001 Jun;2(2):131-42. doi: 10.2174/1389201013378716. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11480418 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and osteoprotegerin-Fc in MC3T3-E1 cells.J Rheum Dis. 2024 Apr 1;31(2):79-85. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0043. Epub 2024 Feb 1. J Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38559798 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoclay gels attenuate BMP2-associated inflammation and promote chondrogenesis to enhance BMP2-spinal fusion.Bioact Mater. 2024 Nov 5;44:474-487. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.10.027. eCollection 2025 Feb. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39559426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amarilio R., Viukov S. V., Sharir A., Eshkar-Oren I., Johnson R. S., Zelzer E. (2007). HIF1α Regulation of Sox9 Is Necessary to Maintain Differentiation of Hypoxic Prechondrogenic Cells during Early Skeletogenesis. Development (Cambridge, England) 134 (21), 3917–3928. 10.1242/dev.008441 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chakkalakal S. A., Uchibe K., Convente M. R., Zhang D., Economides A. N., Kaplan F. S., et al. (2016). Palovarotene Inhibits Heterotopic Ossification and Maintains Limb Mobility and Growth in Mice with the HumanACVR1R206HFibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) Mutation. J. Bone Miner Res. 31 (9), 1666–1675. 10.1002/jbmr.2820 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

