Implantation of Hypoxia-Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cell Advances Therapeutic Angiogenesis
- PMID: 35355589
- PMCID: PMC8958070
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6795274
Implantation of Hypoxia-Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cell Advances Therapeutic Angiogenesis
Abstract
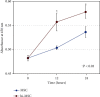
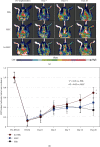
Hypoxia preconditioning enhances the paracrine abilities of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for vascular regeneration and tissue healing. Implantation of hypoxia-induced mesenchymal stem cells (hi-MSCs) may further improve limb perfusion in a murine model of hindlimb ischemia. This study is aimed at determining whether implantation of hi-MSCs is an effective modality for improving outcomes of treatment of ischemic artery diseases. We evaluated the effects of human bone marrow-derived MSC implantation on limb blood flow in an ischemic hindlimb model. hi-MSCs were prepared by cell culture under 1% oxygen for 24 hours prior to implantation. A total of 1 × 105 MSCs and hi-MSCs and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) were intramuscularly implanted into ischemic muscles at 36 hours after surgery. Restoration of blood flow and muscle perfusion was evaluated by laser Doppler perfusion imaging. Blood perfusion recovery, enhanced vessel densities, and improvement of function of the ischemia limb were significantly greater in the hi-MSC group than in the MSC or PBS group. Immunochemistry revealed that hi-MSCs had higher expression levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A than those in MSCs. In addition, an endothelial cell-inducing medium showed high expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1, and von Willebrand factor in hi-MSCs compared to those in MSCs. These findings suggest that pretreatment of MSCs with a hypoxia condition and implantation of hi-MSCs advances neovascularization capability with enhanced therapeutic angiogenic effects in a murine hindlimb ischemia model.
Copyright © 2022 Farina Mohamad Yusoff et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The Department of Stem Cell Biology and Medicine, Graduate School of Biomedical & Health Sciences, Hiroshima University, is a collaborative research laboratory funded by TWOCELLS Company, Limited. All remaining authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived endothelial cells increase capillary density and accelerate angiogenesis in mouse hindlimb ischemia model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jun 8;11(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01710-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32513272 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia pretreatment improves the therapeutic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in hindlimb ischemia via upregulation of NRG-1.Cell Tissue Res. 2022 Apr;388(1):105-116. doi: 10.1007/s00441-021-03562-0. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Cell Tissue Res. 2022. PMID: 35091805
-
Profound Actions of an Agonist of Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone on Angiogenic Therapy by Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Apr;36(4):663-672. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307126. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26868211 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembled GFFYK peptide hydrogel enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse hindlimb ischemia model.Acta Biomater. 2019 Feb;85:94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.12.015. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30550934
-
GDF11 enhances therapeutic functions of mesenchymal stem cells for angiogenesis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Aug 12;12(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02519-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. Retraction in: Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jan 31;14(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03247-1. PMID: 34384486 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoids in lung cancer: Navigating the balance between immunosuppression and therapeutic efficacy.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 4;10(12):e32357. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32357. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of hypoxia-mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of anaerobic bacterial wound infection: wound healing and infection recovery.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 5;14:1251956. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1251956. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37869672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Supportive Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Insulin-Producing Langerhans Islets with a Specific Emphasis on The Secretome.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 18;11(9):2558. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092558. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells for critical limb ischemia: their function, mechanism, and therapeutic potential.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 26;13(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03043-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35883198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-preconditioned bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect neurons from cardiac arrest-induced pyroptosis.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Apr 1;20(4):1103-1123. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01922. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38845218 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

