PML Body Component Sp100A Restricts Wild-Type Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection
- PMID: 35353002
- PMCID: PMC9044927
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00279-22
PML Body Component Sp100A Restricts Wild-Type Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection
Abstract
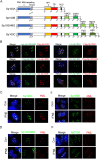
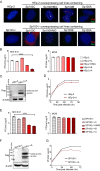
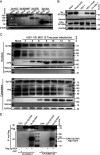
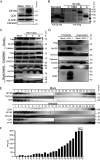
Sp100 (speckled protein 100 kDa) is a constituent component of nuclear structure PML (promyelocytic leukemia) bodies, playing important roles in mediating intrinsic and innate immunity. The Sp100 gene encodes four isoforms with distinct roles in the transcriptional regulation of both cellular and viral genes. Since Sp100 is a primary intranuclear target of infected-cell protein 0 (ICP0), an immediate early E3 ligase encoded by herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), previous investigations attempting to analyze the functions of individual Sp100 variants during HSV-1 infection mostly avoided using a wild-type virus. Therefore, the role of Sp100 under natural infection by HSV-1 remains to be clarified. Here, we reappraised the antiviral capacity of four Sp100 isoforms during infection by a nonmutated HSV-1, examined the molecular behavior of the Sp100 protein in detail, and revealed the following intriguing observations. First, Sp100 isoform A (Sp100A) inhibited wild-type HSV-1 propagation in HEp-2, Sp100-/-, and PML-/- cells. Second, endogenous Sp100 is located in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. During HSV-1 infection, the nuclear Sp100 level decreased drastically upon the detection of ICP0 in the same subcellular compartment, but cytosolic Sp100 remained stable. Third, transfected Sp100A showed subcellular localizations similar to those of endogenous Sp100 and matched the protein size of endogenous cytosolic Sp100. Fourth, HSV-1 infection induced increased secretion of endogenous Sp100 and ectopically expressed Sp100A, which copurified with extracellular vesicles (EVs) but not infectious virions. Fifth, the Sp100A level in secreting cells positively correlated with its level in EVs, and EV-associated Sp100A restricted HSV-1 in recipient cells. IMPORTANCE Previous studies show that the PML body component Sp100 protein is immediately targeted by ICP0 of HSV-1 in the nucleus during productive infection. Therefore, extensive studies investigating the interplay of Sp100 isoforms with HSV-1 were conducted using a mutant virus lacking ICP0 or in the absence of infection. The role of Sp100 variants during natural HSV-1 infection remains blurry. Here, we report that Sp100A potently and independently inhibited wild-type HSV-1 and that during HSV-1 infection, cytosolic Sp100 remained stable and was increasingly secreted into the extracellular space, in association with EVs. Furthermore, the Sp100A level in secreting cells positively correlated with its level in EVs and the anti-HSV-1 potency of these EVs in recipient cells. In summary, this study implies an active antiviral role of Sp100A during wild-type HSV-1 infection and reveals a novel mechanism of Sp100A to restrict HSV-1 through extracellular communications.
Keywords: EVs; HSV-1; PML; Sp100A; cytosolic Sp100; extracellular vesicle; subcellular localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
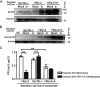
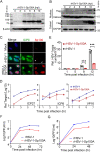
Similar articles
-
Differential functions of interferon-upregulated Sp100 isoforms: herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter-based immediate-early gene suppression and PML protection from ICP0-mediated degradation.J Virol. 2009 May;83(10):5168-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02083-08. Epub 2009 Mar 11. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19279115 Free PMC article.
-
Two overlapping regions within the N-terminal half of the herpes simplex virus 1 E3 ubiquitin ligase ICP0 facilitate the degradation and dissociation of PML and dissociation of Sp100 from ND10.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13287-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02304-13. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24089549 Free PMC article.
-
Differential role of Sp100 isoforms in interferon-mediated repression of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein expression.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(16):8019-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02164-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16873258 Free PMC article.
-
The Fate of Speckled Protein 100 (Sp100) During Herpesviruses Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 1;10:607526. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.607526. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33598438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HSV-1 ubiquitin ligase ICP0: Modifying the cellular proteome to promote infection.Virus Res. 2020 Aug;285:198015. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198015. Epub 2020 May 13. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32416261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Nucleolus and Its Interactions with Viral Proteins Required for Successful Infection.Cells. 2024 Sep 21;13(18):1591. doi: 10.3390/cells13181591. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSV-1 selectively packs the transcription factor Oct-1 into EVs to facilitate its infection.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1205906. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1205906. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37396389 Free PMC article.
-
African Swine Fever Virus Host-Pathogen Interactions.Subcell Biochem. 2023;106:283-331. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-40086-5_11. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 38159232
-
PML Body Component Sp100A Is a Cytosolic Responder to IFN and Activator of Antiviral ISGs.mBio. 2022 Dec 20;13(6):e0204422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02044-22. Epub 2022 Nov 16. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36383022 Free PMC article.
-
A CRISPR-based rapid DNA repositioning strategy and the early intranuclear life of HSV-1.Elife. 2023 Sep 13;12:e85412. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85412. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37702383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szostecki C, Guldner HH, Netter HJ, Will H. 1990. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding a human nuclear antigen predominantly recognized by autoantibodies from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol 145:4338–4347. - PubMed
-
- Guldner HH, Szostecki C, Grotzinger T, Will H. 1992. IFN enhance expression of Sp100, an autoantigen in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol 149:4067–4073. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

