Ritonavir-Boosted Exposure of Kinase Inhibitors: an Open Label, Cross-over Pharmacokinetic Proof-of-Concept Trial with Erlotinib
- PMID: 35352280
- PMCID: PMC8964029
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-022-03244-8
Ritonavir-Boosted Exposure of Kinase Inhibitors: an Open Label, Cross-over Pharmacokinetic Proof-of-Concept Trial with Erlotinib
Abstract
Background: Although kinase inhibitors (KIs) are generally effective, their use has a large impact on the current health care budget. Dosing strategies to reduce treatment costs are warranted. Boosting pharmacokinetic exposure of KIs metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4 with ritonavir might result in lower doses needed and subsequently reduces treatment costs. This study is a proof-of-concept study to evaluate if the dose of erlotinib can be reduced by co-administration with ritonavir.
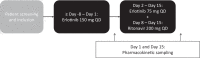
Methods: In this open-label, cross-over study, we compared the pharmacokinetics of monotherapy erlotinib 150 mg once daily (QD) (control arm) with erlotinib 75 mg QD plus ritonavir 200 mg QD (intervention arm). Complete pharmacokinetic profiles at steady-state were taken up to 24 h after erlotinib intake for both dosing strategies.
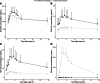
Results: Nine patients were evaluable in this study. For the control arm, the systemic exposure over 24 h, maximum plasma concentration and minimal plasma concentration of erlotinib were 29.3 μg*h/mL (coefficient of variation (CV):58%), 1.84 μg/mL (CV:60%) and 1.00 μg/mL (CV:62%), respectively, compared with 28.9 μg*h/mL (CV:116%, p = 0.545), 1.68 μg/mL (CV:68%, p = 0.500) and 1.06 μg/mL (CV:165%, p = 0.150) for the intervention arm. Exposure to the metabolites of erlotinib (OSI-413 and OSI-420) was statistically significant lower following erlotinib plus ritonavir dosing. Similar results regarding safety in both dosing strategies were observed, no grade 3 or higher adverse event was reported.
Conclusions: Pharmacokinetic exposure at a dose of 75 mg erlotinib when combined with the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor ritonavir is similar to 150 mg erlotinib. Ritonavir-boosting is a promising strategy to reduce erlotinib treatment costs and provides a rationale for other expensive therapies metabolized by CYP3A4.
Keywords: CYP3A4; Erlotinib; pharmacokinetics; pharmacology; ritonavir-boosting.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J. Boosman, C.J. de Gooijer, S.L. Groenland, P. Baas, V. van der Noort and A.D.R. Huitema declare they have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preclinical assessment of the interactions between the antiretroviral drugs, ritonavir and efavirenz, and the tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;76(4):813-9. doi: 10.1007/s00280-015-2856-y. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26330331 Free PMC article.
-
Lopinavir/ritonavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection.Drugs. 2003;63(8):769-802. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00004. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662125 Review.
-
Effect of repeated doses of darunavir plus low-dose ritonavir on the pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in healthy male subjects: phase I randomized, open-label, two-way crossover study.Clin Drug Investig. 2008;28(8):479-85. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200828080-00002. Clin Drug Investig. 2008. PMID: 18598093 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of CYP3A4 inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of maraviroc in healthy volunteers.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Apr;65 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):27-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03133.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18333863 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Darunavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection in adults.Drugs. 2009;69(4):477-503. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969040-00007. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19323590 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic Boosting of Kinase Inhibitors.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 5;15(4):1149. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041149. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of Drug-Drug Interactions Between Ritonavir-Boosted Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) and Targeted Therapy and Supportive Care for Lung Cancer.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023 Feb;4(2):100452. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100452. Epub 2022 Dec 17. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 36568522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faehling M, Schwenk B, Kramberg S, Eckert R, Volckmar A-L, Stenzinger A, et al. Oncogenic driver mutations, treatment, and EGFR-TKI resistance in a Caucasian population with non-small cell lung cancer: survival in clinical practice. Oncotarget. 2017;8(44):77897–77914. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20857. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European medicines agency. Tarceva: EPAR-Product information 2019.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

