Reversible Retinopathy Associated with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor
- PMID: 35350233
- PMCID: PMC8921955
- DOI: 10.1159/000519275
Reversible Retinopathy Associated with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor
Abstract
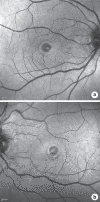
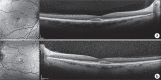
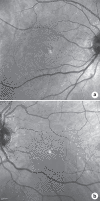
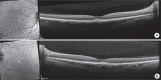
We present a case of reversible, pseudovitelliform lesions while a patient was taking pembrolizumab (PDL-1 inhibitor) and erdafitinib (pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor) outside of clinical trial protocols. A 61-year-old patient with 3 days of metamorphopsia was found to have pseudovitelliform lesions in both eyes 6 weeks after initiation of erdafitinib. After discontinuation of this drug, his visual complaints resolved and his lesions decreased on optical coherence tomography. To our knowledge, this is the first case depicting reversible macular lesions with use of this newly approved medication outside of clinical trial protocols.
Keywords: Fibroblast growth factor receptor; Fibroblast growth factor receptor retinopathy; Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase associated retinopathy; Optical coherence tomography.
Copyright © 2022 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any financial disclosures or conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Optical Coherence Tomography Signs of Erdafitinib-Induced Retinopathy.Cureus. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):e66968. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66968. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280433 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible corneal stromal thinning, acute-onset white cataract and angle-closure glaucoma due to erdafitinib, a fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor: Report of three cases.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2021 Jan;44(1):67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2020.03.018. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2021. PMID: 33162180
-
Optical coherence tomography findings in paraneoplastic pseudovitelliform lesions in melanoma-associated retinopathy.Clin Ophthalmol. 2008 Jun;2(2):461-3. doi: 10.2147/opth.s2282. Clin Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 19668738 Free PMC article.
-
Erdafitinib to treat urothelial carcinoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2019 Aug;55(8):495-501. doi: 10.1358/dot.2019.55.8.3010573. Drugs Today (Barc). 2019. PMID: 31461086 Review.
-
The role of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancers including those of the urinary bladder.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jan;151:104567. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104567. Epub 2019 Nov 23. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 31770593 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety Profile and Adverse Event Management for Futibatinib, An Irreversible FGFR1-4 Inhibitor: Pooled Safety Analysis of 469 Patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 15;30(8):1466-1477. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2646. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38329716 Free PMC article.
-
Serous Retinopathy Associated With Combination MEK and Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor.J Vitreoretin Dis. 2023 Apr 10;7(4):352-355. doi: 10.1177/24741264231163393. eCollection 2023 Jul-Aug. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2023. PMID: 37927314 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Pemigatinib-induced retinopathy: a serial examination of subretinal fluid secondary to an FGFR inhibitor.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 22;3:1247296. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2023.1247296. eCollection 2023. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38983033 Free PMC article.
-
Erdafitinib-Induced Bilateral Multifocal Serous Retinal Detachments and Severe Dry Eye Related Unilateral Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis in a Patient with Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024 May 20;11(6):004556. doi: 10.12890/2024_004556. eCollection 2024. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38846673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loriot Y, Nechhi A, Park SH, Garcia-Donas J, Huddart R, Burgess E, et al. Erdafitinib in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:338–348. - PubMed
-
- van der Noll R, Leijen S, Neuteboom GH, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH. Effect of inhibition of the FGFR-MAPK signaling pathway on the development of ocular toxicities. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39((6)):664–672. - PubMed
-
- Catalani E, Tomassini S, Dal Monte M, Bosco L, Casini G. Localization patterns of fibroblast growth factor 1 and its receptors FGFR1 and FGFR2 in postnatal mouse retina. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;336:423–438. - PubMed
-
- McCannel TA, Chmeilowski B, Finn RS, Goldman J, Ribas A, Wainberg ZA, et al. Bilateral subfoveal neurosensory retinal detachment associated with MEK inhibitor use for metastatic cancer. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132:1005–1009. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

