The transmembrane adapter SCIMP recruits tyrosine kinase Syk to phosphorylate Toll-like receptors to mediate selective inflammatory outputs
- PMID: 35337798
- PMCID: PMC9052152
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101857
The transmembrane adapter SCIMP recruits tyrosine kinase Syk to phosphorylate Toll-like receptors to mediate selective inflammatory outputs
Abstract
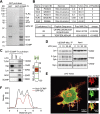
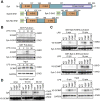
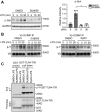
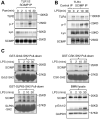
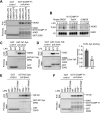
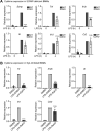
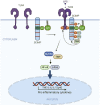
Innate immune signaling by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) involves receptor phosphorylation, which helps to shape and drive key inflammatory outputs, yet our understanding of the kinases and mechanisms that mediate TLR phosphorylation is incomplete. Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) is a nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinase, which is known to relay adaptive and innate immune signaling, including from TLRs. However, TLRs do not contain the conserved dual immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs that typically recruit Syk to many other receptors. One possibility is that the Syk-TLR association is indirect, relying on an intermediary scaffolding protein. We previously identified a role for the palmitoylated transmembrane adapter protein SCIMP in scaffolding the Src tyrosine kinase Lyn, for TLR phosphorylation, but the role of SCIMP in mediating the interaction between Syk and TLRs has not yet been investigated. Here, we show that SCIMP recruits Syk in response to lipopolysaccharide-mediated TLR4 activation. We also show that Syk contributes to the phosphorylation of SCIMP and TLR4 to enhance their binding. Further evidence pinpoints two specific phosphorylation sites in SCIMP critical for its interaction with Syk-SH2 domains in the absence of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. Finally, using inhibitors and primary macrophages from SCIMP-/- mice, we confirm a functional role for SCIMP-mediated Syk interaction in modulating TLR4 phosphorylation, signaling, and cytokine outputs. In conclusion, we identify SCIMP as a novel, immune-specific Syk scaffold, which can contribute to inflammation through selective TLR-driven inflammatory responses.
Keywords: SCIMP; Syk recruitment; TLR4 phosphorylation; inflammation; macrophage.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SCIMP is a universal Toll-like receptor adaptor in macrophages.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Feb;107(2):251-262. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MA0819-138RR. Epub 2019 Aug 29. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31468585
-
Development of SH2 probes and pull-down assays to detect pathogen-induced, site-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of the TLR adaptor SCIMP.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;95(6):564-570. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.10. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28290451
-
SCIMP is a spatiotemporal transmembrane scaffold for Erk1/2 to direct pro-inflammatory signaling in TLR-activated macrophages.Cell Rep. 2021 Sep 7;36(10):109662. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109662. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34496234
-
The SYK side of TLR4: signalling mechanisms in response to LPS and minimally oxidized LDL.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;167(5):990-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02097.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22776094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation in immune cells: direct and indirect effects on toll-like receptor-induced proinflammatory cytokine production.Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(4):347-67. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i4.50. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19673688 Review.
Cited by
-
Imperative role of adaptor proteins in macrophage toll-like receptor signaling pathways.Future Sci OA. 2024 Dec 31;10(1):2387961. doi: 10.1080/20565623.2024.2387961. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Future Sci OA. 2024. PMID: 39248050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
R406 reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil activation.Cell Immunol. 2024 Sep-Oct;403-404:104860. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2024.104860. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Cell Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39084187 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 phosphorylation at tyrosine 672 activates the ERK/c-FOS signaling module for LPS-induced cytokine responses in macrophages.Eur J Immunol. 2023 Jul;53(7):e2250056. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250056. Epub 2023 May 1. Eur J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37058370 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the multifaceted role of toll-like receptors in immunity of aquatic animals: pioneering strategies for disease management.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1378111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378111. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvant activity of tubeimosides by mediating the local immune microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 10;14:1108244. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1108244. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36845089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon S. Pattern recognition receptors: Doubling up for the innate immune response. Cell. 2002;111:927–930. - PubMed
-
- Akira S., Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Sabroe I., Read R.C., Whyte M.K., Dockrell D.H., Vogel S.N., Dower S.K. Toll-like receptors in health and disease: Complex questions remain. J. Immunol. 2003;171:1630–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

