CYP1A2 mRNA Expression Rather than Genetic Variants Indicate Hepatic CYP1A2 Activity
- PMID: 35335907
- PMCID: PMC8954692
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030532
CYP1A2 mRNA Expression Rather than Genetic Variants Indicate Hepatic CYP1A2 Activity
Abstract
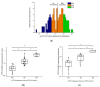
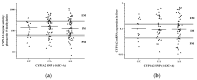
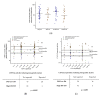
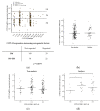
CYP1A2, one of the most abundant hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes, is involved in metabolism of several drugs and carcinogenic compounds. Data on the significance of CYP1A2 genetic polymorphisms in enzyme activity are highly inconsistent; therefore, the impact of CYP1A2 genetic variants (−3860G>A, −2467delT, −739T>G, −163C>A, 2159G>A) on mRNA expression and phenacetin O-dealkylation selective for CYP1A2 was investigated in human liver tissues and in psychiatric patients belonging to Caucasian populations. CYP1A2*1F, considered to be associated with high CYP1A2 inducibility, is generally identified by the presence of −163C>A polymorphism; however, we demonstrated that −163C>A existed in several haplotypes (CYP1A2*1F, CYP1A2*1L, CYP1A2*1M, CYP1A2*1V, CYP1A2*1W), and consequently, CYP1A2*1F was a much rarer allelic variant (0.4%) than reported in Caucasian populations. Of note, −163C>A polymorphism was found to result in an increase of neither mRNA nor the activity of CYP1A2. Moreover, hepatic CYP1A2 activity was associated with hepatic or leukocyte mRNA expression rather than genetic polymorphisms of CYP1A2. Consideration of non-genetic phenoconverting factors (co-medication with CYP1A2-specific inhibitors/inducers, tobacco smoking and non-specific factors, including amoxicillin+clavulanic acid therapy or chronic alcohol consumption) did not much improve genotype−phenotype estimation. In conclusion, CYP1A2-genotyping is inappropriate for the prediction of CYP1A2 function; however, CYP1A2 mRNA expression in leukocytes can inform about patients’ CYP1A2-metabolizing capacity.
Keywords: CYP1A2; CYP1A2 expression; CYP1A2 genetic polymorphisms; amoxicillin+clavulanic acid; carbamazepine; chronic alcohol consumption; ciprofloxacin; non-genetic factors; phenacetin O-dealkylation activity; smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of CYP1A2 by heavy coffee consumption is associated with the CYP1A2 -163C>A polymorphism.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;66(7):697-703. doi: 10.1007/s00228-010-0823-4. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20390257
-
Comparisons of CYP1A2 genetic polymorphisms, enzyme activity and the genotype-phenotype relationship in Swedes and Koreans.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Jun;63(6):537-46. doi: 10.1007/s00228-007-0288-2. Epub 2007 Mar 17. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17370067
-
Haplotypes in the 5'-untranslated region of the CYP1A2 gene are inversely associated with lung cancer risk but do not correlate with caffeine metabolism.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2013 Mar;54(2):124-32. doi: 10.1002/em.21747. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2013. PMID: 23138776
-
Rapid genotyping for relevant CYP1A2 alleles by pyrosequencing.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Dec;61(12):887-92. doi: 10.1007/s00228-005-0029-3. Epub 2005 Nov 24. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16307269 Review.
-
Insights into the substrate specificity, inhibitors, regulation, and polymorphisms and the clinical impact of human cytochrome P450 1A2.AAPS J. 2009 Sep;11(3):481-94. doi: 10.1208/s12248-009-9127-y. Epub 2009 Jul 10. AAPS J. 2009. PMID: 19590965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of the CYP2D6 and CYP1A2 Gene Polymorphisms on Response to Duloxetine in Patients with Major Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 30;24(17):13459. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713459. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686266 Free PMC article.
-
CYP1A2 expression rather than genotype is associated with olanzapine concentration in psychiatric patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 28;13(1):18507. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45752-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37898643 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Phosphorus, Serum Bicarbonate, and Renal Function in Relation to Liver CYP1A2 Activity.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 19;13(18):2996. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13182996. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761363 Free PMC article.
-
Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Amoxicillin-Clavulanate: Spotlight on Gut Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome and Bile Acid Profile in Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 22;25(13):6863. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136863. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38999973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimada T., Yamazaki H., Mimura M., Inui Y., Guengerich F.P. Interindividual variations in human liver cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved in the oxidation of drugs, carcinogens and toxic chemicals: Studies with liver microsomes of 30 Japanese and 30 Caucasians. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994;270:414–423. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa M., Nishimura M., Ogino D., Chiba R., Ikai I., Ueda N., Naito S., Kuribayashi S., Moustafa M.A., Uchida T., et al. Cytochrome P450 gene expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in comparison with the liver. Cancer Sci. 2004;95:520–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb03243.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

