Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Chronic Degenerative Diseases: New Metabolic Targets in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 35328633
- PMCID: PMC8949044
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063212
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Chronic Degenerative Diseases: New Metabolic Targets in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
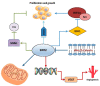
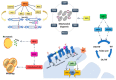
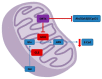
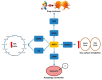
Sirtuins (SIRTs) are a family of class III histone deacetylases (HDACs) consisting of seven members, widely expressed in mammals. SIRTs mainly participate in metabolic homeostasis, DNA damage repair, cell survival, and differentiation, as well as other cancer-related biological processes. Growing evidence shows that SIRTs have pivotal roles in chronic degenerative diseases, including colorectal cancer (CRC), the third most frequent malignant disease worldwide. Metabolic alterations are gaining attention in the context of CRC development and progression, with mitochondrion representing a crucial point of complex and intricate molecular mechanisms. Mitochondrial SIRTs, SIRT2, SIRT3, SIRT4 and SIRT5, control mitochondrial homeostasis and dynamics. Here, we provide a comprehensive review on the latest advances on the role of mitochondrial SIRTs in the initiation, promotion and progression of CRC. A deeper understanding of the pathways by which mitochondrial SIRTs control CRC metabolism may provide new molecular targets for future innovative strategies for CRC prevention and therapy.
Keywords: SIRT2; SIRT3; SIRT4; SIRT5; chronic degenerative diseases; colorectal cancer; metabolism; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Mitochondrial Sirtuins (SIRT3, SIRT4 and SIRT5) in Renal Cell Metabolism: Implication for Kidney Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 25;25(13):6936. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136936. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial sirtuins, metabolism, and aging.J Genet Genomics. 2022 Apr;49(4):287-298. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 34856390 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Cancer: A Revisited Review from Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies.Theranostics. 2024 May 11;14(7):2993-3013. doi: 10.7150/thno.97320. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38773972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial sirtuins: Energy dynamics and cancer metabolism.Mol Cells. 2024 Feb;47(2):100029. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100029. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Mol Cells. 2024. PMID: 38331199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting sirtuins for cancer therapy: epigenetics modifications and beyond.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 14;14(17):6726-6767. doi: 10.7150/thno.100667. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39479446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Value of Serum SIRT1 Combined with Uterine Hemodynamics in Predicting Disease Severity and Fetal Growth Restriction in Preeclampsia.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Apr 7;2023:1744625. doi: 10.1155/2023/1744625. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9848149. doi: 10.1155/2023/9848149 PMID: 37064953 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Gut aging: A wane from the normal to repercussion and gerotherapeutic strategies.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 12;10(19):e37883. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37883. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial fusion-fission dynamics and its involvement in colorectal cancer.Mol Oncol. 2024 May;18(5):1058-1075. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13578. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38158734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2 inhibitor promotes mitochondrial dysfunction and ER-phagy in colorectal cancer cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 May 29;29(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00599-1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38811901 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT3 Modulates Endothelial Mitochondrial Redox State during Insulin Resistance.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 19;11(8):1611. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081611. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009329 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

