Thioredoxin Domain Containing 5 Suppression Elicits Serum Amyloid A-Containing High-Density Lipoproteins
- PMID: 35327511
- PMCID: PMC8945230
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030709
Thioredoxin Domain Containing 5 Suppression Elicits Serum Amyloid A-Containing High-Density Lipoproteins
Abstract
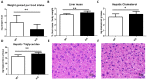
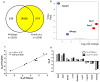
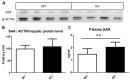
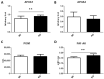
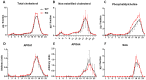
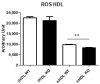
Thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5) is a protein disulfide isomerase involved in several diseases related to oxidative stress, energy metabolism and cellular inflammation. In a previous manuscript, a negative association between fatty liver development and hepatic Txndc5 expression was observed. To study the role of TXNDC5 in the liver, we generated Txndc5-deficient mice. The absence of the protein caused an increased metabolic need to gain weight along with a bigger and fatter liver. RNAseq was performed to elucidate the putative mechanisms, showing a substantial liver overexpression of serum amyloid genes (Saa1, Saa2) with no changes in hepatic protein, but discrete plasma augmentation by the gene inactivation. Higher levels of malonyldialdehyde, apolipoprotein A1 and platelet activating factor-aryl esterase activity were also found in serum from Txndc5-deficient mice. However, no difference in the distribution of high-density lipoproteins (HDL)-mayor components and SAA was found between groups, and even the reactive oxygen species decreased in HDL coming from Txndc5-deficient mice. These results confirm the relation of this gene with hepatic steatosis and with a fasting metabolic derive remedying an acute phase response. Likewise, they pose a new role in modulating the nature of HDL particles, and SAA-containing HDL particles are not particularly oxidized.
Keywords: HDL; RNAseq; SAA; Saa1; Saa2; TXNDC5; Txndc5-deficient mice; liver; serum amyloid; thioredoxin domain containing 5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin Domain Containing 5 (TXNDC5): Friend or Foe?Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 4;46(4):3134-3163. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040197. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein TXNDC5 Interacts with PRDX6 and HSPA9 to Regulate Glutathione Metabolism and Lipid Peroxidation in the Hepatic AML12 Cell Line.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17131. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417131. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138960 Free PMC article.
-
Differential plasma clearance of murine acute-phase serum amyloid A proteins SAA1 and SAA2.Biochem J. 1997 Mar 1;322 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):663-9. doi: 10.1042/bj3220663. Biochem J. 1997. PMID: 9065791 Free PMC article.
-
A newly discovered teleost disulfide isomerase, thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5), from big-belly seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis): Insights into its molecular and functional properties and immune regulatory functions.Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Jan;114:103827. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103827. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32805308
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Aug 8;27(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00770-4. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35934705 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin Domain Containing 5 (TXNDC5): Friend or Foe?Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 4;46(4):3134-3163. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040197. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein TXNDC5 Interacts with PRDX6 and HSPA9 to Regulate Glutathione Metabolism and Lipid Peroxidation in the Hepatic AML12 Cell Line.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17131. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417131. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138960 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

