Gut Microbiome in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Role
- PMID: 35327352
- PMCID: PMC8945462
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030550
Gut Microbiome in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Role
Abstract
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered to be a significant health threat globally, and has attracted growing concern in the research field of liver diseases. NAFLD comprises multifarious fatty degenerative disorders in the liver, including simple steatosis, steatohepatitis and fibrosis. The fundamental pathophysiology of NAFLD is complex and multifactor-driven. In addition to viruses, metabolic syndrome and alcohol, evidence has recently indicated that the microbiome is related to the development and progression of NAFLD. In this review, we summarize the possible microbiota-based therapeutic approaches and highlight the importance of establishing the diagnosis of NAFLD through the different spectra of the disease via the gut-liver axis.
Keywords: NAFLD; microbial functions; microbiota; microbiota-based approach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
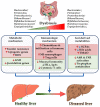
Similar articles
-
Oral and Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Central Role of Porphyromonas gingivalis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 2;9:822190. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.822190. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35308549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Gut-Liver Axis in Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis Associated NAFLD and NAFLD-HCC.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 23;10(3):524. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030524. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota, fatty liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Res. 2018 Mar;2(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.11.005. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Liver Res. 2018. PMID: 30416839 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota and their metabolites in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatoma Res. 2021 Jan 13;7:11. doi: 10.20517/2394-5079.2020.134. eCollection 2021. Hepatoma Res. 2021. PMID: 33490737 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the metabolic syndrome and paving the way for microRNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.FEBS J. 2014 Jun;281(11):2503-24. doi: 10.1111/febs.12806. Epub 2014 Apr 28. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24702768 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota-derived indole compounds attenuate metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by improving fat metabolism and inflammation.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2307568. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2307568. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38299316 Free PMC article.
-
Urbanization associates with restricted gut microbiome diversity and delayed maturation in infants.iScience. 2023 Oct 6;26(11):108136. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108136. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37876823 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Chlorogenic Acid in the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Animal Studies and Clinical Trials-A Narrative Review.Metabolites. 2024 Jun 20;14(6):346. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060346. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between oral microbiota, gut microbiota and systematic diseases.J Oral Microbiol. 2023 May 15;15(1):2213112. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2023.2213112. eCollection 2023. J Oral Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37200866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of perilipin 5 deficiency on gut microbiome profiles in murine metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and MAFLD-hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 14;14:1443654. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1443654. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39469452 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- Hallym University Research Fund/Hallym University Research Fund
- NRF-2018M3A9F3020956, NRF-2019R1I1A3A01060447, NRF-2020R1I1A3073530 and NRF-2020R1A6A1A03043026/Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

