Dietary Polyphenols as Therapeutic Intervention for Alzheimer's Disease: A Mechanistic Insight
- PMID: 35326204
- PMCID: PMC8945272
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030554
Dietary Polyphenols as Therapeutic Intervention for Alzheimer's Disease: A Mechanistic Insight
Abstract
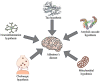
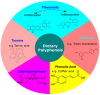
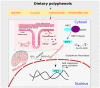
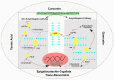
Dietary polyphenols encompass a diverse range of secondary metabolites found in nature, such as fruits, vegetables, herbal teas, wine, and cocoa products, etc. Structurally, they are either derivatives or isomers of phenol acid, isoflavonoids and possess hidden health promoting characteristics, such as antioxidative, anti-aging, anti-cancerous and many more. The use of such polyphenols in combating the neuropathological war raging in this generation is currently a hotly debated topic. Lately, Alzheimer's disease (AD) is emerging as the most common neuropathological disease, destroying the livelihoods of millions in one way or another. Any therapeutic intervention to curtail its advancement in the generation to come has been in vain to date. Using dietary polyphenols to construct the barricade around it is going to be an effective strategy, taking into account their hidden potential to counter multifactorial events taking place under such pathology. Besides their strong antioxidant properties, naturally occurring polyphenols are reported to have neuroprotective effects by modulating the Aβ biogenesis pathway in Alzheimer's disease. Thus, in this review, I am focusing on unlocking the hidden secrets of dietary polyphenols and their mechanistic advantages to fight the war with AD and related pathology.
Keywords: amyloid; homeostasis; like curcumin; metal chelation; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanistic insights into the potential role of dietary polyphenols and their nanoformulation in the management of Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 May;174:116376. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116376. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38508080 Review.
-
Polyphenols as therapeutic molecules in Alzheimer's disease through modulating amyloid pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Apr;51(2):466-79. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8722-9. Epub 2014 May 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24826916 Review.
-
Cholinesterase targeting by polyphenols: A therapeutic approach for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Sep;24(9):753-762. doi: 10.1111/cns.12971. Epub 2018 May 16. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29770579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel role of red wine-derived polyphenols in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease dementia and brain pathology: experimental approaches and clinical implications.Planta Med. 2012 Oct;78(15):1614-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1315377. Epub 2012 Sep 21. Planta Med. 2012. PMID: 23023952 Review.
-
Dietary polyphenols for treatment of Alzheimer's disease--future research and development.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(4):330-42. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666140813122703. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25312617 Review.
Cited by
-
Is Caperatic Acid the Only Compound Responsible for Activity of Lichen Platismatia glauca within the Nervous System?Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;11(10):2069. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102069. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290793 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids as Promising Neuroprotectants and Their Therapeutic Potential against Alzheimer's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 28;2022:6038996. doi: 10.1155/2022/6038996. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36071869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishing network pharmacology between natural polyphenols and Alzheimer's disease using bioinformatic tools - An advancement in Alzheimer's research.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Aug 23;13:101715. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101715. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39280991 Free PMC article.
-
Role of BDNF Signaling in the Neuroprotective and Memory-enhancing Effects of Flavonoids in Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(8):984-995. doi: 10.2174/1871527323666230912090856. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37702162 Review.
-
In the quest for the ideal sweetener: Aspartame exacerbates selected biomarkers in the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) model of Alzheimer's disease more than sucrose.Aging Brain. 2023 Jul 30;4:100090. doi: 10.1016/j.nbas.2023.100090. eCollection 2023. Aging Brain. 2023. PMID: 37559954 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

