The Role of Nitric Oxide in Stem Cell Biology
- PMID: 35326146
- PMCID: PMC8944807
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11030497
The Role of Nitric Oxide in Stem Cell Biology
Abstract
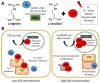
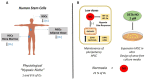
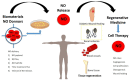
Nitric oxide (NO) is a gaseous biomolecule endogenously synthesized with an essential role in embryonic development and several physiological functions, such as regulating mitochondrial respiration and modulation of the immune response. The dual role of NO in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) has been previously reported, preserving pluripotency and cell survival or inducing differentiation with a dose-dependent pattern. In this line, high doses of NO have been used in vitro cultures to induce focused differentiation toward different cell lineages being a key molecule in the regenerative medicine field. Moreover, optimal conditions to promote pluripotency in vitro are essential for their use in advanced therapies. In this sense, the molecular mechanisms underlying stemness regulation by NO have been studied intensively over the current years. Recently, we have reported the role of low NO as a hypoxia-like inducer in pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), which supports using this molecule to maintain pluripotency under normoxic conditions. In this review, we stress the role of NO levels on stem cells (SCs) fate as a new approach for potential cell therapy strategies. Furthermore, we highlight the recent uses of NO in regenerative medicine due to their properties regulating SCs biology.
Keywords: biomaterials; cell differentiation; cell signaling; evolution; metabolism; nitric oxide; pluripotency; regenerative medicine; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of nitric oxide in the maintenance of pluripotency and regulation of the hypoxia response in stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Apr 26;7(3):605-17. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i3.605. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25914767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of mitochondrial function and endoplasmic reticulum stress by nitric oxide in pluripotent stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2017 Feb 26;9(2):26-36. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i2.26. World J Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 28289506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stemness of Human Pluripotent Cells: Hypoxia-Like Response Induced by Low Nitric Oxide.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 2;10(9):1408. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091408. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573040 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in embryonic stem cell and induced pluripotent stem cell differentiation in male germ cells.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):12278-12289. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27990. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30536380 Review.
-
Nitric Oxide And Hypoxia Response In Pluripotent Stem Cells.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:417-418. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.09.024. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 28162281
Cited by
-
Succinate as a New Actor in Pluripotency and Early Development?Metabolites. 2022 Jul 15;12(7):651. doi: 10.3390/metabo12070651. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35888775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide: an old drug but with new horizons in ophthalmology-a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Aug 30;11(10):352. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5634. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37675299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NIR-Triggered Release of Nitric Oxide by Upconversion-Based Nanoplatforms to Enhance Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteoporosis Therapy.Biomater Res. 2024 Jul 22;28:0058. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0058. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39040622 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus Alters the Immuno-Expression of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Rat Pancreas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4974. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094974. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563364 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular delivery of nitric oxide enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells for myocardial infarction.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec;9(48):eadi9967. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi9967. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38019911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moncada S., Palmer R.M., Higgs E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991;43:109–142. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

