Nematode chromosomes
- PMID: 35323874
- PMCID: PMC9071541
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyac014
Nematode chromosomes
Abstract
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has shed light on many aspects of eukaryotic biology, including genetics, development, cell biology, and genomics. A major factor in the success of C. elegans as a model organism has been the availability, since the late 1990s, of an essentially gap-free and well-annotated nuclear genome sequence, divided among 6 chromosomes. In this review, we discuss the structure, function, and biology of C. elegans chromosomes and then provide a general perspective on chromosome biology in other diverse nematode species. We highlight malleable chromosome features including centromeres, telomeres, and repetitive elements, as well as the remarkable process of programmed DNA elimination (historically described as chromatin diminution) that induces loss of portions of the genome in somatic cells of a handful of nematode species. An exciting future prospect is that nematode species may enable experimental approaches to study chromosome features and to test models of chromosome evolution. In the long term, fundamental insights regarding how speciation is integrated with chromosome biology may be revealed.
Keywords: WormBook; centromere; holocentric; meiosis; programmed DNA elimination; repetitive DNA; synteny; telomere.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures

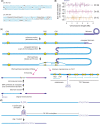

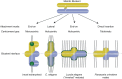

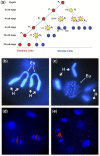

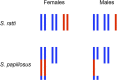
Similar articles
-
A telomere-to-telomere assembly of Oscheius tipulae and the evolution of rhabditid nematode chromosomes.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Jan 18;11(1):jkaa020. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaa020. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33561231 Free PMC article.
-
The role of chromosome ends during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans.Bioessays. 1996 Jun;18(6):447-52. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180606. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8787533
-
Strong nucleosomes reside in meiotic centromeres of C. elegans.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015;33(2):365-73. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2013.879263. Epub 2014 Mar 6. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015. PMID: 24601792
-
The roles of transcription, chromatin organisation and chromosomal processes in holocentromere establishment and maintenance.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul;127:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35042676 Review.
-
Comparative Genomics of Sex, Chromosomes, and Sex Chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans and Other Nematodes.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2802:455-472. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3838-5_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38819568 Review.
Cited by
-
Programmed DNA elimination in the parasitic nematode Ascaris.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Feb 2;19(2):e1011087. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011087. eCollection 2023 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36730159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Hope: A Hermaphroditic Nematode Enables Analysis of a Recent Whole Genome Duplication Event.Genome Biol Evol. 2022 Dec 7;14(12):evac169. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evac169. Genome Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 36461901 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome fusion and programmed DNA elimination shape karyotypes of parasitic nematodes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 23:2023.12.21.572835. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.21.572835. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Curr Biol. 2024 May 20;34(10):2147-2161.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.04.022 PMID: 38187595 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Remarkable chromosomes and karyotypes: A top 10 list.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Apr 1;35(4):pe1. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-12-0498. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38517328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome fusion and programmed DNA elimination shape karyotypes of nematodes.Curr Biol. 2024 May 20;34(10):2147-2161.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.04.022. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 38688284
References
-
- Ahmed S, Hodgkin J.. MRT-2 checkpoint protein is required for germline immortality and telomere replication in C. elegans. Nature. 2000;403(6766):159–164. - PubMed
-
- Albertson DG, Nwaorgu OC, Sulston JE.. Chromatin diminution and a chromosomal mechanism of sexual differentiation in Strongyloides papillosus. Chromosoma. 1979;75(1):75–87. - PubMed
-
- Albertson DG, Rose AM, Villeneuve AM.. Chromosome organization, mitosis, and meiosis. In: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, editors. C. elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor (NY: ): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Albertson DG, Thomson JN.. The kinetochores of Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma. 1982;86(3):409–428. - PubMed

