Nanotherapeutics and the Brain
- PMID: 35320699
- PMCID: PMC9236656
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-092220-030853
Nanotherapeutics and the Brain
Abstract
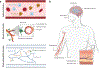
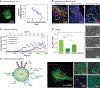
Brain disease remains a significant health, social, and economic burden with a high failure rate of translation of therapeutics to the clinic. Nanotherapeutics have represented a promising area of technology investment to improve drug bioavailability and delivery to the brain, with several successes for nanotherapeutic use for central nervous system disease that are currently in the clinic. However, renewed and continued research on the treatment of neurological disorders is critically needed. We explore the challenges of drug delivery to the brain and the ways in which nanotherapeutics can overcome these challenges. We provide a summary and overview of general design principles that can be applied to nanotherapeutics for uptake and penetration in the brain. We next highlight remaining questions that limit the translational potential of nanotherapeutics for application in the clinic. Lastly, we provide recommendations for ongoing preclinical research to improve the overall success of nanotherapeutics against neurological disease.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; brain delivery; brain distribution; brain parenchyma; nanomedicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanomedicine based strategies for oligonucleotide traversion across the blood-brain barrier.J Control Release. 2023 Feb;354:554-571. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.031. Epub 2023 Jan 19. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 36649742 Review.
-
Nanotherapeutics for Alzheimer's Disease with Preclinical Evaluation and Clinical Trials: Challenges, Promises and Limitations.Curr Drug Deliv. 2022;19(1):17-31. doi: 10.2174/1567201818666210910162750. Curr Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 34514990 Review.
-
Overcoming the Blood-Brain Barrier: The Role of Nanomaterials in Treating Neurological Diseases.Adv Mater. 2018 Nov;30(46):e1801362. doi: 10.1002/adma.201801362. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 30066406 Review.
-
Nanotherapeutics: An insight into healthcare and multi-dimensional applications in medical sector of the modern world.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1521-1537. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.026. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29793315 Review.
-
Nanotherapeutics in the EU: an overview on current state and future directions.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Feb 19;9:1005-23. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S55359. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24600222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Models of the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier and Their Applications in the Development and Research of (Neuro)Pharmaceuticals.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 18;14(8):1729. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081729. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Intrathecal Nanoparticle Delivery: Targeting the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier for Enhanced CNS Drug Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;17(8):1070. doi: 10.3390/ph17081070. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preserving and enhancing mitochondrial function after stroke to protect and repair the neurovascular unit: novel opportunities for nanoparticle-based drug delivery.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jul 7;17:1226630. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1226630. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37484823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Finger S 2005. Minds Behind the Brain: A History of the Pioneers and Their Discoveries. Oxford, UK: Oxford Univ. Press
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Carter JL. 2014. Multiple sclerosis: current and emerging disease-modifying therapies and treatment strategies. Mayo Clin. Proc 89:225–40 - PubMed
-
- UN Dep. Econ. Soc. Aff. Popul. Div. 2019. World population ageing 2019: highlights. Publ., ST/ESA/SER.A/430, United Nat., New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

